Introduction
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses store, process, and access data, shifting IT operations from rigid, on-premises infrastructures to highly scalable, on-demand platforms. From Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) to Software as a Service (SaaS), organizations are leveraging cloud solutions to drive efficiency, accelerate innovation, and reduce costs.
However, securing cloud environments presents unique challenges. Unlike traditional on-premises security models, cloud security follows a shared responsibility framework, where both cloud providers and customers play crucial roles in safeguarding data. Additionally, increasing cyber threats, complex compliance mandates, and risks such as misconfigurations and insider threats make cloud security a critical priority for enterprises.
This white paper explores the evolving threat landscape, compliance requirements, and best practices for securing cloud environments, ensuring businesses can harness the full potential of the cloud without compromising security.
Key Risks in Cloud Security
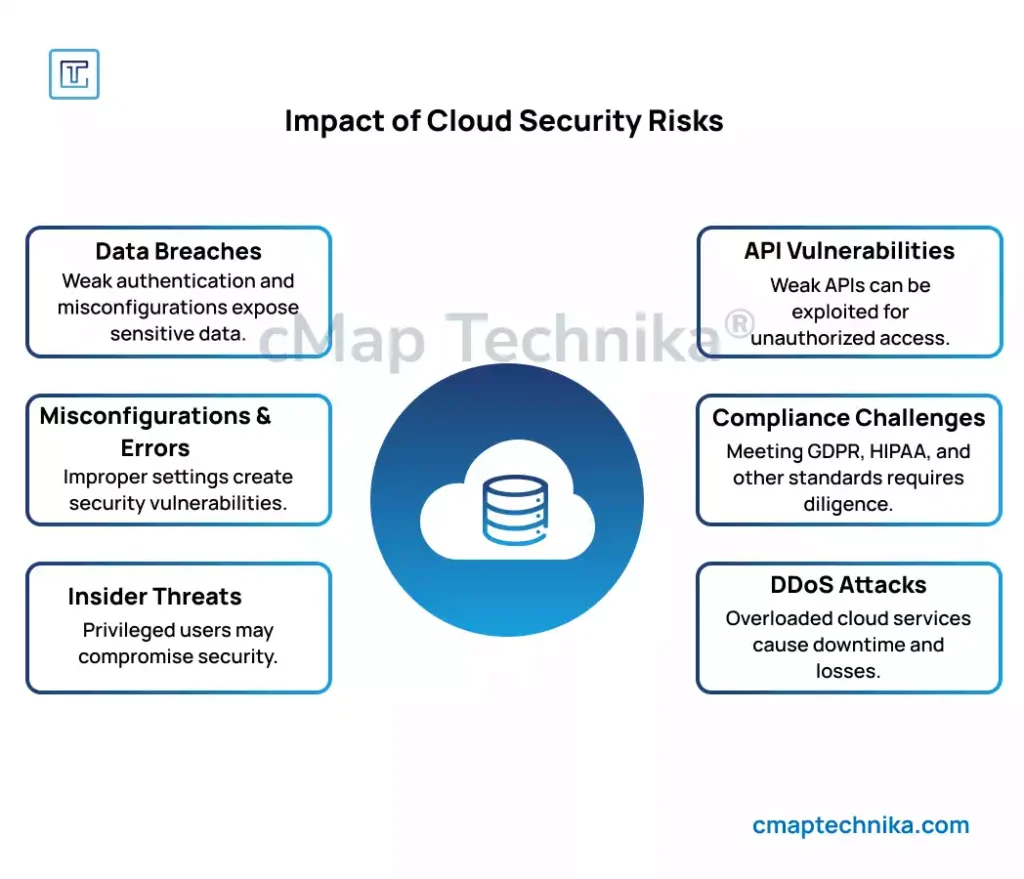
Despite its benefits, the cloud introduces several security risks that organizations must address:
1. Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Cloud storage and databases are prime targets for cybercriminals. Misconfigured permissions, weak authentication, and lack of encryption can expose sensitive business and customer data.
2. Misconfigurations and Human Error
Many security incidents stem from misconfigured cloud services. A single overlooked setting, such as an open storage bucket or improperly defined access controls, can lead to significant vulnerabilities.
3. Insider Threats
Employees, contractors, or partners with privileged access can intentionally or accidentally compromise cloud security, leading to data loss, fraud, or operational disruptions.
4. API Security Gaps
APIs facilitate communication between cloud services, but poorly secured APIs can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to cloud environments and manipulate data.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Challenges
Organizations operating in regulated industries must comply with frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. Cloud providers offer compliance tools, but responsibility for data security remains with the business.
6. DDoS Attacks and Service Disruptions
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can overwhelm cloud-based applications, leading to downtime and loss of revenue. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in cloud-hosted services to disrupt operations.
Cloud Security Compliance Frameworks
Adopting industry standards and frameworks helps organizations maintain security and compliance in cloud environments.
- ISO/IEC 27001 – Establishes an information security management system (ISMS) to protect cloud data.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework – Provides guidelines for risk management in cloud environments.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – Governs data protection and privacy for companies operating in the EU.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) – Ensures the security of healthcare data stored in the cloud.
- Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) STAR Certification – Offers best practices for cloud security and risk management.
Advanced Security Strategies for Cloud Environments
To effectively protect cloud assets, organizations must implement multi-layered security strategies that address the unique challenges of cloud computing. Below are key approaches that enhance cloud security and resilience:
1. Zero Trust Security Model
A Zero Trust approach ensures that no user, device, or application is trusted by default—every access request must be verified continuously. This model significantly reduces attack surfaces and insider threats.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Enforce least privilege access, role-based access control (RBAC), and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent unauthorized access.
- Micro-Segmentation: Divide cloud workloads into isolated zones to contain potential breaches and prevent lateral movement of attackers.
- Continuous Monitoring: Deploy AI-driven threat detection to analyze user behavior, detect anomalies, and prevent unauthorized access in real time.
2. Encryption and Data Protection
Securing sensitive data is critical to cloud security, especially with remote access and multi-cloud storage. Strong encryption methods and advanced data protection techniques ensure confidentiality and compliance.
- End-to-End Encryption: Encrypt data at rest, in transit, and during processing to safeguard against breaches.
- Tokenization: Replace sensitive information with unique tokens, reducing exposure without compromising functionality.
- Secure Key Management: Use cloud-native or third-party key management systems (KMS) to securely store and rotate encryption keys.
3. Automated Threat Detection and Response
Cloud security threats are constantly evolving, requiring proactive threat detection and automated response mechanisms to mitigate risks.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Aggregates and analyzes security logs from multiple sources to detect suspicious activity.
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR): Uses AI-powered analytics to correlate security data across endpoints, workloads, and cloud services.
- Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs): Monitors virtual machines, containers, and serverless workloads for vulnerabilities and attacks.
4. Secure DevOps (DevSecOps) Practices
Security should be integrated into every stage of software development, ensuring that applications remain secure from deployment to runtime.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Security: Automate security configurations to detect and remediate misconfigurations before deployment.
- Continuous Security Testing: Implement automated vulnerability scans, static code analysis, and penetration testing throughout the CI/CD pipeline.
- Container Security: Use Kubernetes security policies, runtime protection, and image scanning to secure cloud-native applications.
5. Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Security
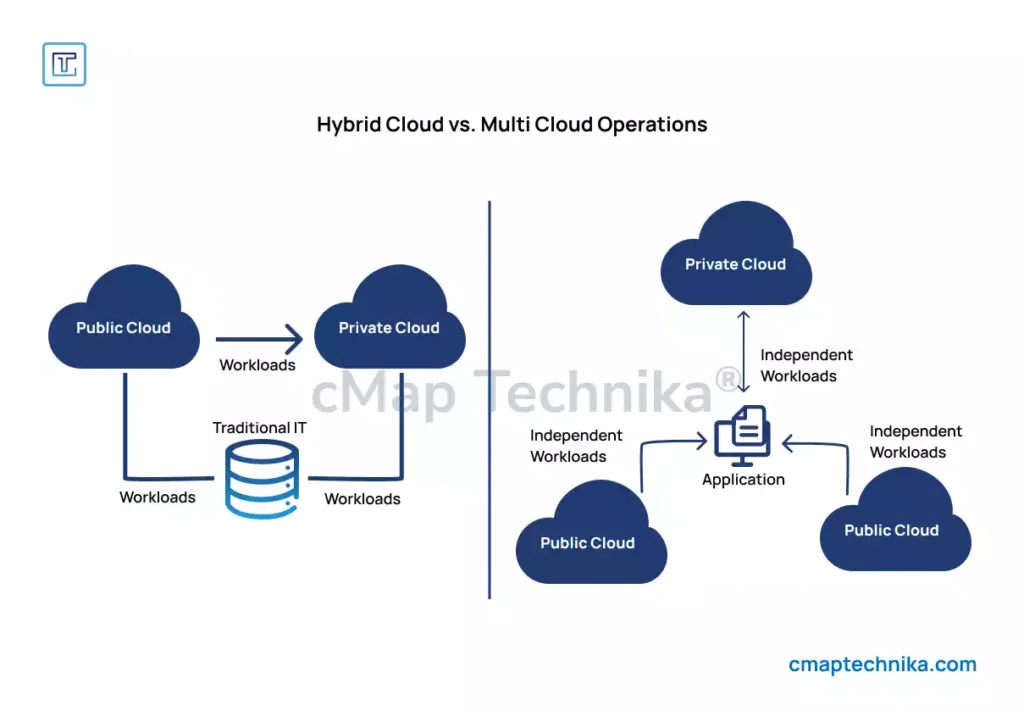
Organizations frequently operate across multiple cloud providers or integrate on-premises and cloud environments. A unified security approach ensures consistency and minimizes risk.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Automates compliance monitoring, risk assessment, and remediation for cloud configurations.
- Unified Security Policies: Standardizes security controls across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and hybrid environments.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): Provides visibility, policy enforcement, and data protection for cloud applications.
By implementing these advanced security strategies, organizations can enhance resilience, ensure regulatory compliance, and proactively defend against cloud-based threats while enabling seamless cloud transformation.
Conclusion: Securing the Future of Cloud Computing
As businesses accelerate their cloud transformation, security can no longer be an afterthought—it must be an integral part of the strategy. A resilient cloud security framework requires a proactive, multi-layered approach that incorporates Zero Trust principles, robust encryption, automated threat detection, and strict regulatory compliance.
By embracing AI-driven security solutions, real-time monitoring, and continuous risk assessments, organizations can stay ahead of emerging threats while maintaining operational agility. Leveraging the right security tools and best practices not only mitigates risks but also enhances resilience, strengthens data integrity, and ensures business continuity.
In a digital landscape where threats evolve rapidly, a well-secured cloud ecosystem is not just a protective measure—it’s a competitive advantage that enables innovation, fosters trust, and supports sustainable growth. Businesses that prioritize security today will be best positioned to navigate the challenges of tomorrow.
About Waltcorp
Waltcorp specializes in cloud transformation, security consulting, and enterprise IT solutions. Our expertise in cloud security ensures that businesses can innovate confidently while protecting their critical assets. Contact us today to learn how we can help secure your cloud infrastructure.






