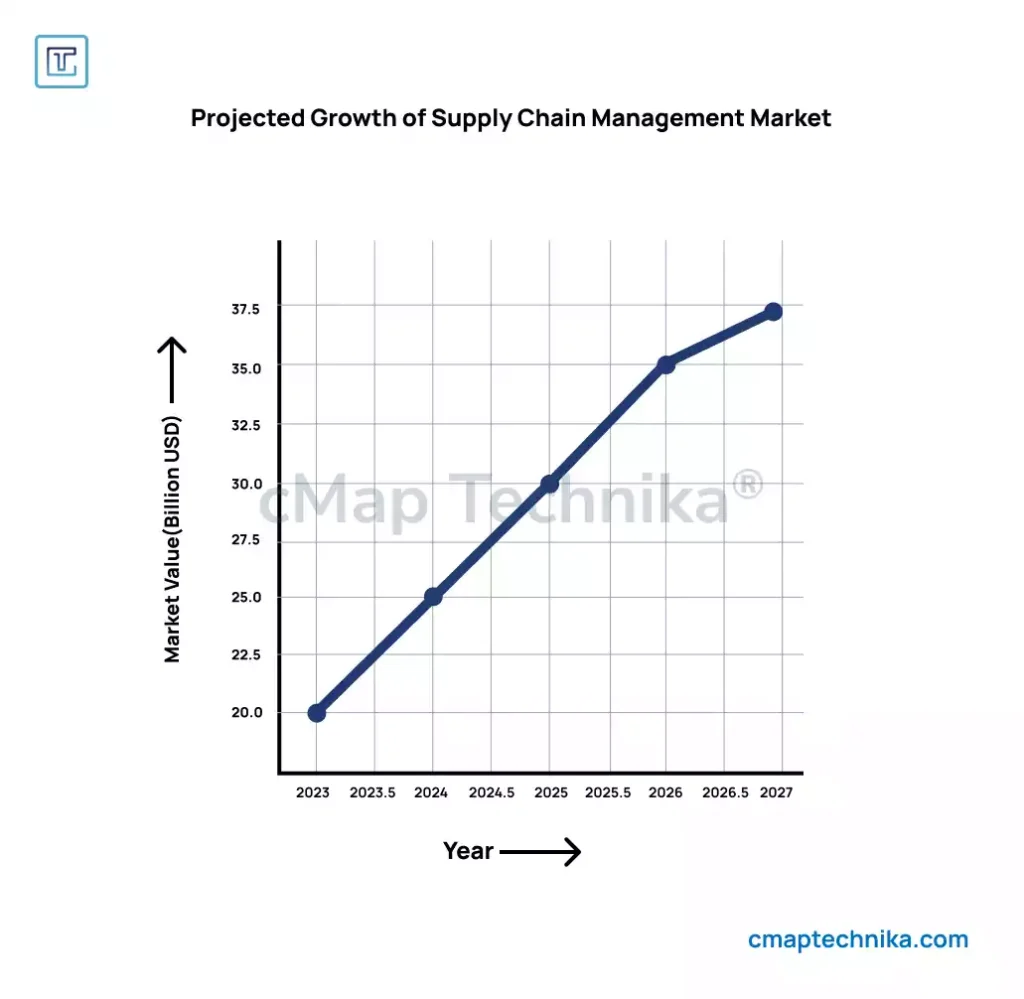
The modern supply chain is no longer a simple process of moving goods from point A to point B. It has evolved into a complex, interconnected network where efficiency and innovation go hand in hand to meet the demands of global markets. As businesses face challenges like rising customer expectations, geopolitical instability, and the push for sustainability, optimizing supply chain operations has become a strategic priority. Smarter supply chain strategies are essential to creating lean, resilient, and efficient systems capable of driving growth in an unpredictable world.
This article explores how innovative approaches to supply chain management can unlock new opportunities, streamline processes, and enable businesses to thrive in competitive environments.
The Foundations of an Efficient Supply Chain
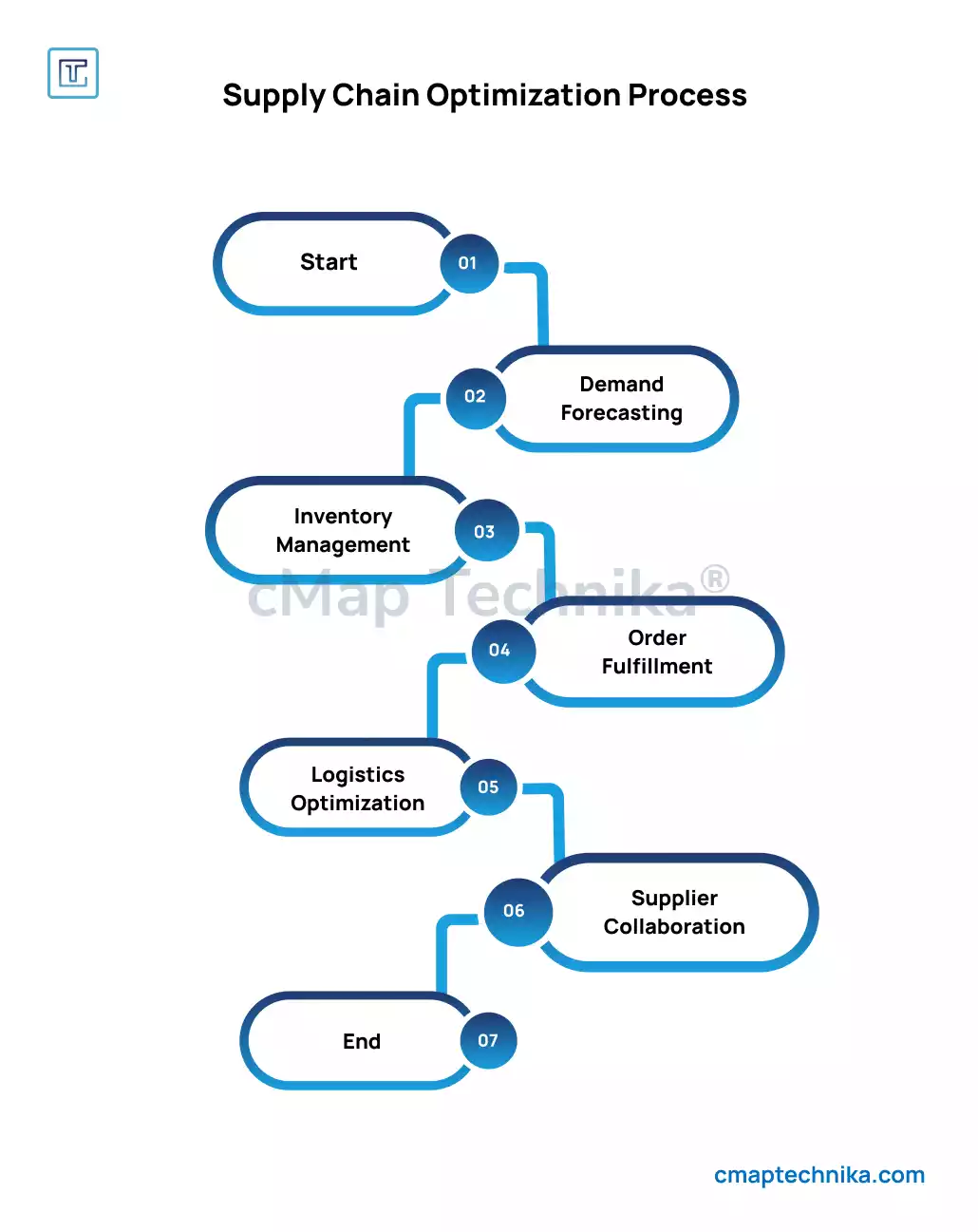
Efficiency in the supply chain is a cornerstone of operational excellence. It’s about achieving the maximum output with the least possible input—delivering products and services to the right place, at the right time, and at the lowest possible cost while maintaining quality and customer satisfaction. Achieving this balance requires a deep understanding of the supply chain’s core components: procurement, production, distribution, and logistics.
Traditional supply chain operations often focus on minimizing costs through bulk purchasing, centralized production, and standardized distribution. While these methods can reduce expenses, they may not always align with the agility and customization demanded by today’s markets. Modern supply chains, in contrast, prioritize flexibility, data-driven decision-making, and collaboration.
For example, a consumer electronics company must respond quickly to changes in demand, ensure timely delivery of components, and maintain strict quality controls. A delay in one part of the chain—such as sourcing microchips—can disrupt the entire process, highlighting the need for streamlined operations.
The Role of Technology in Supply Chain Optimization
Innovation is revolutionizing supply chain management by introducing advanced tools and technologies that enhance efficiency. Technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and predictive analytics are transforming how businesses operate. These innovations enable better visibility, faster decision-making, and improved risk management across the supply chain.
Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
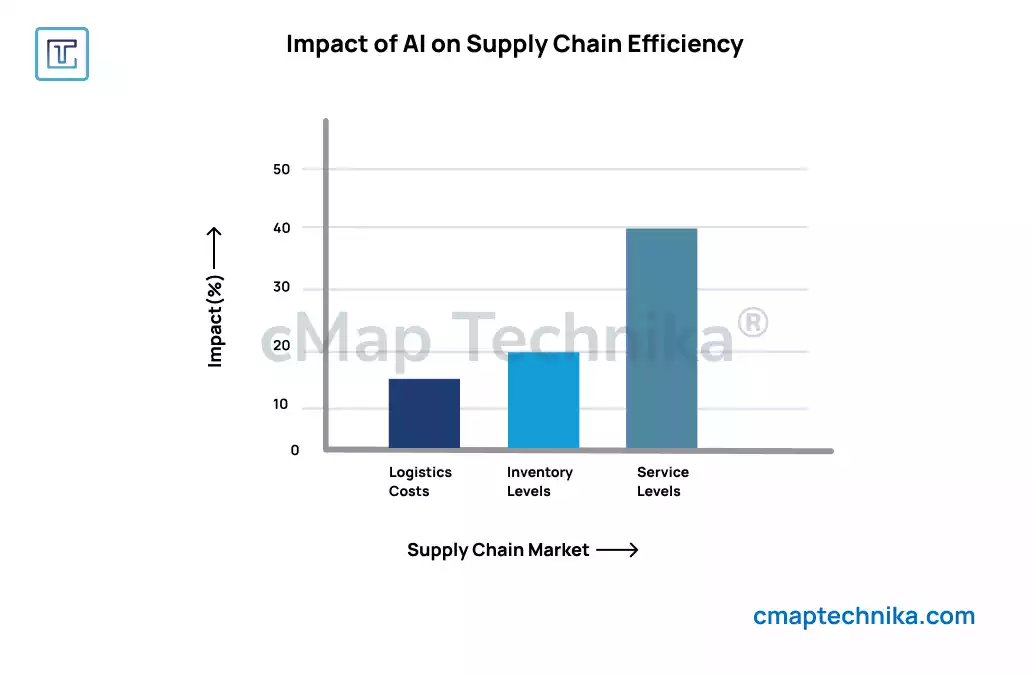
AI and predictive analytics play a pivotal role in identifying patterns, forecasting demand, and optimizing inventory levels. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical data to predict future trends, allowing businesses to prepare for seasonal spikes, unexpected disruptions, or shifts in consumer behavior.
Take the case of a global retailer leveraging AI to manage inventory. By predicting demand for specific products in different regions, the company can allocate resources more effectively, reducing overstock and minimizing shortages. This level of precision not only saves costs but also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability.
Blockchain for Transparency and Security
Blockchain technology addresses one of the supply chain’s most critical challenges: transparency. By creating a secure, immutable record of transactions, blockchain enables real-time tracking of goods and materials. This ensures that stakeholders across the supply chain can verify the origin, movement, and condition of products at every stage.
For instance, in the food industry, blockchain allows consumers to trace the journey of their groceries, from farm to table. This level of transparency builds trust, reduces fraud, and helps companies comply with stringent regulatory standards.
The Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices, such as smart sensors and GPS trackers, provide real-time data on the location and condition of goods. This information enables businesses to monitor shipments, optimize routes, and respond proactively to delays or disruptions.
Consider a logistics company using IoT-enabled trucks to monitor temperature-sensitive cargo, such as pharmaceuticals. Real-time temperature readings allow the company to take corrective action if conditions deviate from acceptable ranges, ensuring the safe delivery of products.
Building Resilience in Supply Chain Operations
Resilience is a critical component of a modern supply chain. In an era of frequent disruptions, from natural disasters to global pandemics, businesses must ensure that their supply chains can withstand shocks and recover quickly.
Diversification of Suppliers
Relying on a single supplier or region for critical materials can expose businesses to significant risks. Diversifying suppliers and sourcing materials from multiple locations reduces dependence and ensures continuity in case of disruptions.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, companies that had diversified their supply chains were better equipped to handle supply shortages and maintain production. By contrast, those reliant on a single source faced significant delays and financial losses.
Digital Twins and Scenario Planning
Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical supply chain processes—allow businesses to simulate different scenarios and test strategies before implementing them. This technology enables organizations to identify vulnerabilities, evaluate potential risks, and make informed decisions.
For instance, a manufacturer can use a digital twin to assess the impact of a supplier delay on production schedules and explore alternative solutions, such as reallocating resources or expediting shipments.
Sustainability: The Future of Supply Chain Optimization
As environmental concerns take center stage, sustainability has become a key focus in supply chain optimization. Companies are adopting eco-friendly practices to reduce their carbon footprint, minimize waste, and align with consumer values.
Green Logistics
Green logistics involves optimizing transportation networks to reduce emissions and energy consumption. This includes strategies such as consolidating shipments, using fuel-efficient vehicles, and adopting alternative energy sources like electric trucks.
For example, a major e-commerce company committed to achieving carbon-neutral deliveries by investing in electric delivery vehicles and optimizing delivery routes. These initiatives not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also enhance brand reputation.
Circular Supply Chains
Circular supply chains emphasize reusing, recycling, and repurposing materials to create a closed-loop system. This approach reduces waste, conserves resources, and extends the lifecycle of products.
A fashion brand adopting circular supply chain practices might collect used clothing from customers, recycle the materials, and incorporate them into new designs. This model not only reduces environmental impact but also appeals to eco-conscious consumers.
Collaborative Strategies for Supply Chain Excellence
Collaboration is essential for optimizing supply chain operations. By fostering partnerships with suppliers, distributors, and technology providers, businesses can achieve greater efficiency and innovation.
Vendor Collaboration
Strong relationships with suppliers are crucial for ensuring timely deliveries and maintaining quality standards. Collaborative planning, forecasting, and replenishment (CPFR) is a practice that involves sharing data and insights with suppliers to align operations and avoid bottlenecks.
For example, an automotive company working closely with its parts suppliers can coordinate production schedules and inventory levels, reducing lead times and minimizing disruptions.
Integration with Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
Outsourcing logistics to 3PL providers allows businesses to leverage specialized expertise and resources. These providers offer services such as warehousing, transportation, and distribution, enabling companies to focus on their core competencies.
A consumer goods company partnering with a 3PL provider might use the latter’s advanced warehousing and distribution network to streamline operations and reach customers more efficiently.
Conclusion
Optimizing supply chain operations is no longer just about cost-cutting—it is about creating systems that are efficient, innovative, and resilient. By embracing advanced technologies, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing sustainability, businesses can transform their supply chains into strategic assets that drive growth and competitiveness.
The future of supply chain management lies in its ability to adapt to changing demands, mitigate risks, and deliver value to customers and stakeholders. Organizations that invest in smarter supply chain strategies are not only positioning themselves for success but also contributing to a more sustainable and interconnected global economy.
In a rapidly evolving world, the supply chain stands as both a challenge and an opportunity. Businesses that view it as a dynamic ecosystem rather than a linear process will unlock its full potential, ensuring their place in a thriving, resilient future.







