Introduction
The life sciences industry is undergoing a transformative shift, driven by the convergence of cutting-edge technologies, evolving regulatory frameworks, and a pressing need to expedite drug development. Traditional pharmaceutical R&D is fraught with challenges—protracted timelines, escalating costs, and high failure rates in clinical trials. However, companies are now embracing innovative solutions such as artificial intelligence (AI), real-world data (RWD), digital twin simulations, and decentralized clinical trials to streamline drug discovery and bring life-saving treatments to market faster.
The COVID-19 pandemic served as a catalyst for unprecedented advancements in R&D efficiency, demonstrating that rapid innovation is possible without compromising safety. This article explores how industry leaders—Pfizer, Moderna, and Roche—have successfully optimized their R&D pipelines through AI-driven analytics, adaptive trial models, and data-driven decision-making. Each case study showcases the unique strategies these companies employed to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and accelerate regulatory approvals. Finally, we analyze the comparative strengths of their approaches and extract key lessons for the future of drug development.
Case Study 1: Pfizer’s AI-Driven Drug Discovery and Accelerated Vaccine Development
Overview
Pfizer, a global leader in pharmaceuticals, has pioneered AI-driven drug discovery and accelerated clinical development through innovative research methodologies. The company’s rapid development of the COVID-19 vaccine in collaboration with BioNTech stands as a testament to the power of AI, mRNA technology, and digital twin simulations in expediting drug development.
Key Strategies Implemented
1. AI-Driven Target Identification and Molecular Screening
Pfizer employs AI and machine learning (ML) to identify promising drug candidates and optimize molecular screening.
- AI algorithms analyze massive biological datasets to predict the most effective drug-target interactions.
- High-throughput screening automates the assessment of thousands of compounds, reducing research time significantly.
2. mRNA Technology and Rapid Vaccine Development
Pfizer’s breakthrough COVID-19 vaccine, Comirnaty, was developed using mRNA technology, enabling rapid iteration and production.
- Traditional vaccine development takes 8–10 years, but mRNA platforms allow swift prototype creation.
- AI-driven simulation models optimize vaccine stability and enhance immune response predictions.
3. Digital Twin Technology for Clinical Trials
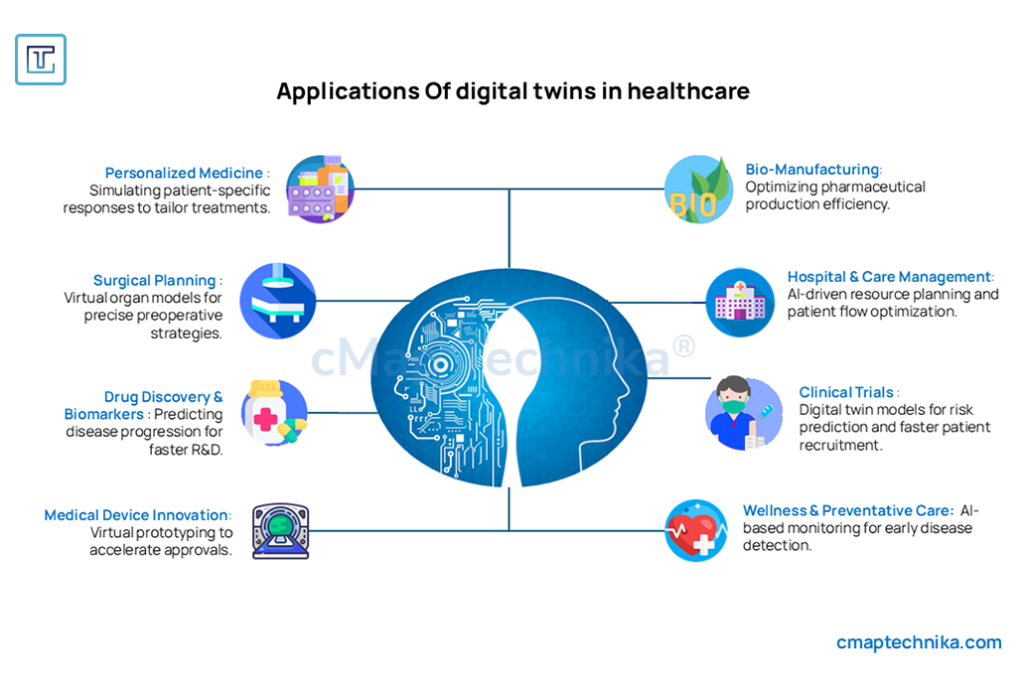
Pfizer leveraged digital twins to simulate clinical trials, refining study protocols before real-world implementation.
- AI-driven patient recruitment reduced enrollment time by 30%.
- Predictive models helped mitigate trial risks, increasing the likelihood of regulatory success.
Impact and Outcomes
- Development Timeline: Reduced from an industry average of 10 years to less than 1 year for the COVID-19 vaccine.
- Cost Savings: AI-driven drug discovery significantly cut preclinical research costs.
- Regulatory Success: Fast-tracked FDA approval and global vaccine rollout.
Case Study 2: Moderna’s Agile R&D Model and AI-Powered Drug Development
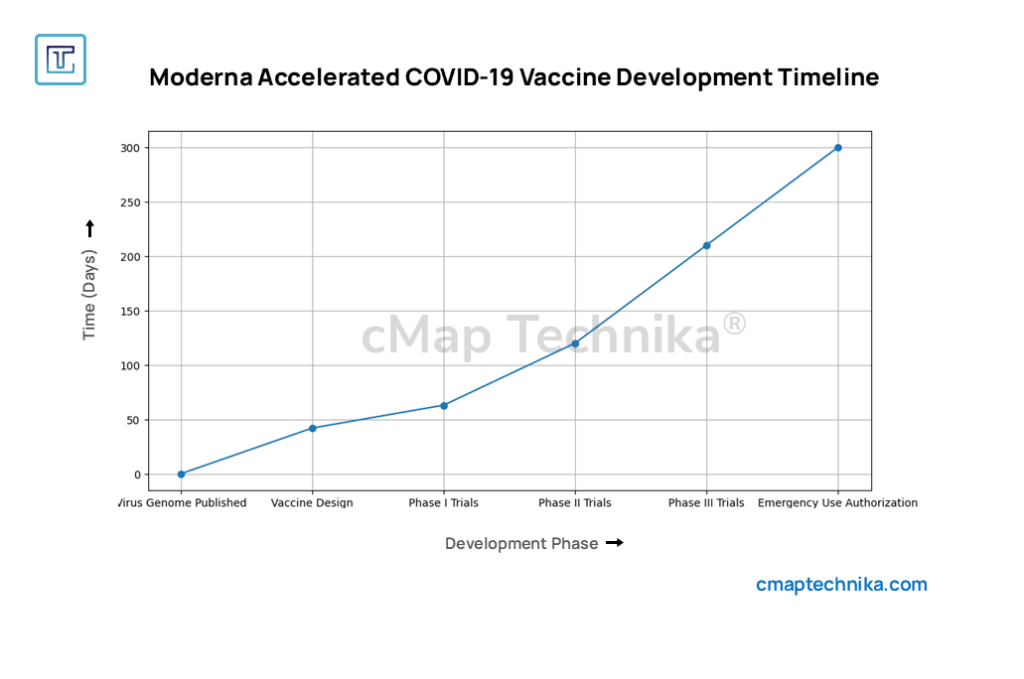
Overview
Moderna, a biotechnology disruptor, has redefined R&D through an AI-centric approach, cloud-based research infrastructure, and automated laboratory workflows. The company’s rapid adaptation of AI and mRNA technology underscores its ability to streamline development while fostering innovation.
Key Strategies Implemented
1. Cloud-Based AI and Computational Biology
Moderna’s digital-first R&D approach accelerates drug discovery and design.
- AI models analyze genomic sequences and optimize mRNA structures for enhanced stability.
- Cloud computing enables real-time collaboration among research teams worldwide.
2. mRNA Platform for Personalized Therapeutics
Moderna’s modular mRNA platform is designed for scalable vaccine and therapeutic development.
- The core technology is now applied to cancer vaccines and rare disease treatments.
- AI-assisted analytics refine mRNA sequences for improved efficacy.
3. Decentralized and Adaptive Clinical Trials
Moderna integrates remote monitoring and AI-driven trial oversight to enhance efficiency.
- Wearable health devices collect real-time patient data for adaptive analysis.
- AI-based compliance monitoring reduces protocol deviations, ensuring data integrity.
Impact and Outcomes
- Speed: Reduced vaccine development timelines from years to months.
- Cost Efficiency: Automated workflows minimized operational expenses.
- Regulatory Milestones: Rapid FDA approvals due to real-time adaptive trial models.
Case Study 3: Roche’s AI-Driven Biomarker Discovery and Personalized Medicine Strategy
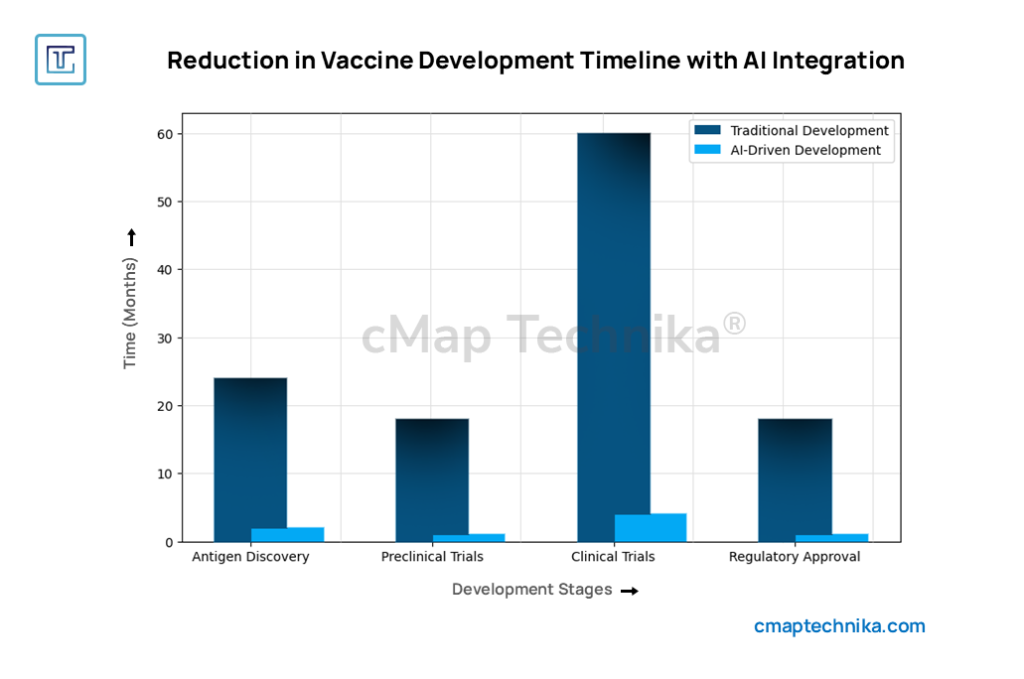
Overview
Roche has positioned itself as a leader in precision medicine by leveraging AI, multi-omics data analysis, and real-world evidence to optimize drug development and treatment personalization.
Key Strategies Implemented
1. AI-Enhanced Biomarker Discovery
Roche employs AI-powered genomic sequencing to uncover disease-related biomarkers.
- Machine learning algorithms analyze genetic variations to identify optimal drug targets.
- AI-driven predictive models assess patient responses to specific therapies.
2. Integration of Real-World Evidence (RWE) in Drug Development
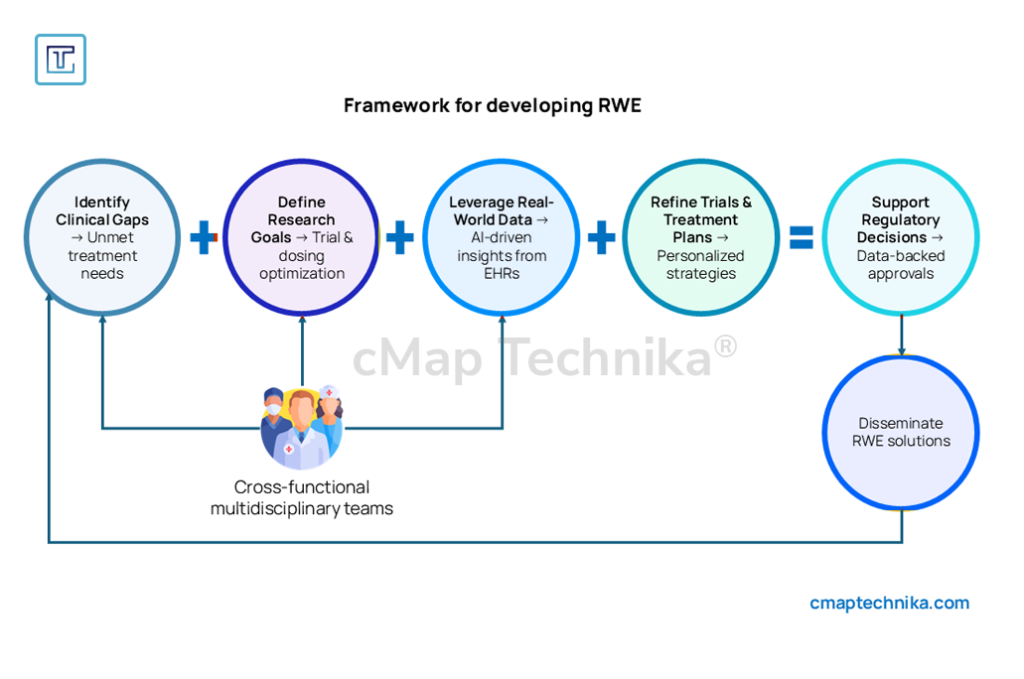
Roche leverages RWE to refine clinical trial design and treatment protocols.
- AI extracts insights from electronic health records (EHRs) to inform trial modifications.
- RWE-based dosing strategies improve patient-specific treatment plans.
3. AI-Powered Digital Pathology and Imaging
Roche integrates AI-driven pathology solutions to enhance diagnostics and oncology treatments.
- Deep learning models improve cancer detection and prognosis assessment.
- AI-assisted imaging enhances the accuracy of tumor characterization.
Impact and Outcomes
- Personalized Medicine Success: AI-enhanced biomarker discovery led to multiple targeted therapy approvals.
- Clinical Trial Efficiency: AI-driven patient stratification improved success rates.
- Regulatory Advancements: RWE integration expedited approvals for groundbreaking treatments.
Conclusion
The R&D strategies employed by Pfizer, Moderna, and Roche demonstrate how AI, mRNA technology, and data-driven analytics are reshaping drug development. Each company has leveraged these tools uniquely: Pfizer excels in AI-driven vaccine innovation and digital twin modeling, Moderna leads in cloud-based AI infrastructure and rapid iteration, and Roche stands out in precision medicine through biomarker discovery and real-world evidence integration.
A key takeaway from these case studies is the role of timing and adaptability in optimizing R&D. Pfizer’s swift collaboration with BioNTech enabled it to pioneer mRNA vaccines in record time, while Moderna’s agile infrastructure allowed it to replicate and refine the model across multiple therapeutic areas. Roche’s long-term investment in AI-driven precision medicine showcases how predictive analytics can guide personalized treatments.
Looking ahead, the integration of AI, decentralized trials, and real-world data will continue to drive efficiency, cost reduction, and improved patient outcomes. The future of life sciences R&D will depend on the ability to balance speed with precision, leveraging digital transformation to revolutionize drug discovery and development.