Introduction
The life sciences industry operates in one of the most heavily regulated environments globally. From drug development to medical devices and biotechnology advancements, companies must navigate a complex web of regulatory requirements that vary across regions and evolve continuously. Balancing compliance with the imperative for innovation is a formidable challenge, yet a well-defined regulatory strategy can transform compliance from a burden into a competitive advantage. This white paper explores the key regulatory challenges faced by life sciences companies and presents a strategic framework to maintain compliance while fostering innovation.
The Evolving Regulatory Landscape
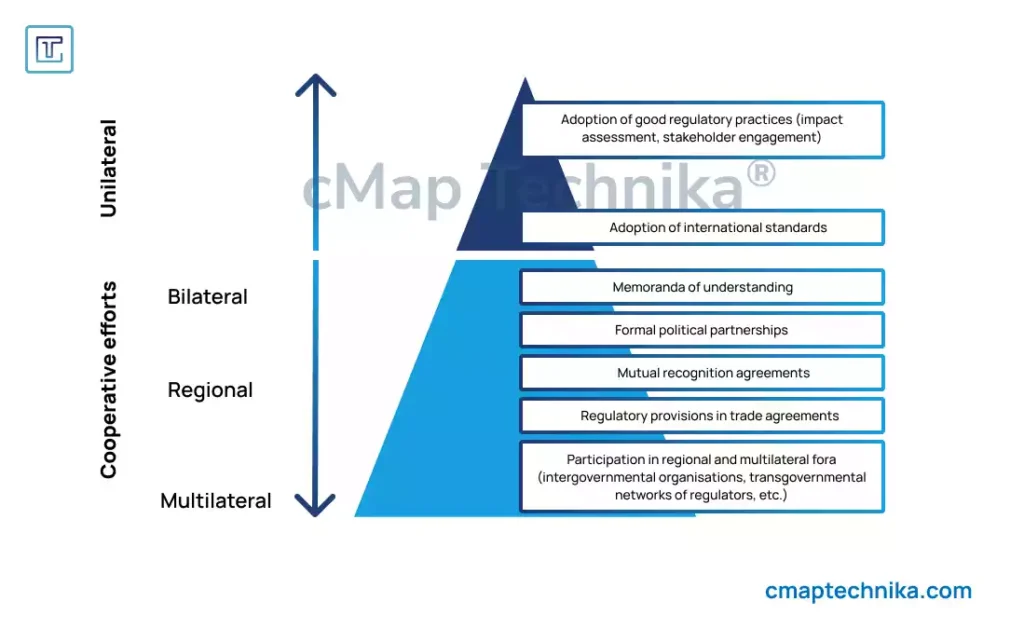
1. Global Regulatory Divergence
Regulatory agencies worldwide, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) in Japan, impose distinct requirements for drug approval, medical device certification, and biotechnology advancements.
Challenges:
- Harmonization Difficulties: Companies seeking global expansion must comply with different standards, which can slow down product launches.
- Changing Regulations: Regulatory policies often shift in response to emerging technologies, requiring constant vigilance and adaptation.
- Varying Data Requirements: The type and volume of clinical data required differ between regions, leading to additional testing and regulatory hurdles.
Example:
Moderna, a U.S.-based biotech firm, encountered delays in launching its COVID-19 vaccine in Europe due to differing regulatory requirements between the FDA and EMA. The EMA required additional data on the vaccine’s stability, which was not mandated by the FDA. By proactively engaging with both regulators and modifying their study protocols early, Moderna reduced approval timelines and ensured a smoother rollout.
2. Digital Transformation and Regulatory Compliance
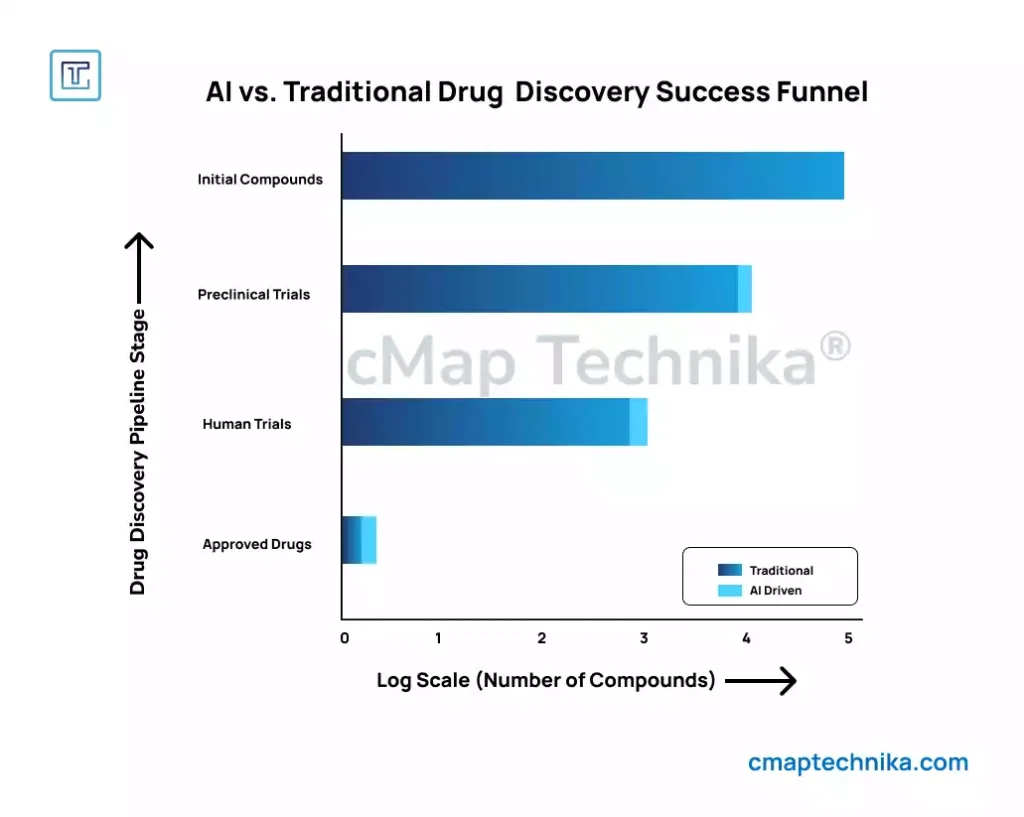
With the integration of AI-driven drug discovery, personalized medicine, and digital therapeutics, regulatory agencies are adapting their frameworks to accommodate emerging technologies. However, regulatory uncertainty surrounding digital tools can create compliance challenges.
Considerations:
- AI and Machine Learning in Drug Discovery: Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA require transparency in AI-driven decision-making for drug approvals.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: Compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and other data protection laws is critical for handling patient data, especially in telemedicine and AI-driven diagnostics.
- Regulatory Adaptation to Digital Health: FDA’s Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) framework sets new compliance expectations for digital therapeutics and medical software.
Example:
Pfizer, which employs AI for drug repurposing, had to adjust its regulatory submissions when authorities requested explainability of AI-generated results. By developing transparent AI models and engaging in early regulatory discussions, Pfizer expedited approvals for its AI-discovered drug candidates.
3. Evolving Clinical Trial Requirements
The landscape of clinical trials is undergoing significant shifts, with increasing adoption of decentralized trials, adaptive trial designs, and post-market surveillance mandates.
Key Trends:
- Decentralized Trials: Telemedicine and wearable devices enable remote patient monitoring but require new compliance protocols.
- Real-World Evidence (RWE): Regulatory agencies increasingly accept RWE for faster approvals, necessitating robust data collection strategies.
- Post-Market Safety Monitoring: Pharmacovigilance requirements demand ongoing data collection beyond traditional trials.
Example:
AstraZeneca conducted a decentralized clinical trial for lung cancer treatment by integrating cloud-based patient monitoring. The company worked closely with regulatory agencies to obtain pre-approvals for telehealth methodologies, reducing regulatory hurdles and improving trial efficiency.
Strategic Compliance Framework
1. Proactive Regulatory Intelligence
Regulatory compliance must be forward-thinking rather than reactive. Establishing regulatory intelligence teams and leveraging AI-powered analytics can help companies anticipate regulatory changes.
Best Practices:
- Establish a global regulatory affairs team to monitor evolving guidelines and regulatory trends.
- Invest in AI-powered regulatory monitoring tools to track legislative changes across multiple regions.
- Develop strong industry partnerships to gain early insights into upcoming regulatory shifts and collaborate with stakeholders.
Example:
GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) integrated predictive analytics into its regulatory operations using Smartsheet, a cloud-based project management tool. This enhanced their ability to track regulatory changes in real-time, allowing them to adjust clinical trial designs and streamline approval processes.
2. Risk-Based Compliance Management
A risk-based approach to compliance enables companies to allocate resources effectively by focusing on high-risk areas.
Implementation:
- Quality Risk Management (QRM) Systems: Assess the probability and impact of regulatory non-compliance.
- Regular Compliance Audits: Conduct self-assessments to identify weak spots before regulators do.
- Cross-Functional Regulatory Review Boards: Establish teams across R&D, compliance, and legal to ensure a holistic approach.
Example:
Editas Medicine, a biotech firm specializing in CRISPR gene-editing, employed risk-based compliance management to preemptively address ethical concerns. By working closely with regulators, the company ensured smoother approval processes for its gene-editing therapies.
3. Integration of Compliance into Innovation Pipelines
Embedding compliance considerations early in the product lifecycle ensures that innovation is aligned with regulatory expectations.
Strategies:
- Regulatory Involvement in Early R&D: Engage compliance teams from the concept phase to align with evolving regulatory standards.
- Use of Digital Twins in Regulatory Testing: Simulating real-world scenarios can preemptively address regulatory concerns and streamline approval processes.
Example:
Medtronic, a medical device company, integrated regulatory risk assessments into the initial prototype development process for its MiniMed insulin pumps. This proactive approach reduced approval times and ensured compliance from the start.
4. Digital Tools for Regulatory Reporting and Compliance
Regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions can streamline compliance management and improve reporting accuracy.
Key Tools:
- Automated Compliance Tracking: AI-driven platforms that flag potential compliance issues in real-time.
- Electronic Submission Platforms: Simplifies document submissions to regulatory agencies, reducing manual errors.
- Blockchain-Based Data Integrity Systems: Enhances transparency and traceability in clinical trials and drug development.
Example:
Moderna implemented blockchain-based clinical trial data tracking, significantly reducing documentation errors and expediting regulatory approvals.
5. Strengthening Regulatory-Agency Engagement
Early and continuous dialogue with regulatory agencies can facilitate smoother approvals and accelerate time-to-market.
Engagement Tactics:
- Pre-submission Meetings: Gain early feedback on potential compliance concerns, reducing the risk of later-stage delays.
- Adaptive Pathways and Accelerated Approval Programs: Utilize regulatory frameworks that support faster approvals for breakthrough therapies.
- Regulatory Collaboration Initiatives: Participate in collaborative regulatory forums and working groups to stay ahead of policy changes.
Example:
Biogen leveraged the FDA’s Breakthrough Therapy Designation for its Alzheimer’s drug, Aduhelm. By engaging in multiple pre-submission consultations, the company reduced approval time by nearly two years.
Conclusion
Regulatory complexity in the life sciences industry is not a challenge to be avoided but an opportunity to build competitive advantage through strategic compliance. Companies that proactively integrate regulatory intelligence, risk-based compliance management, and digital transformation into their operations will not only navigate evolving regulations effectively but also drive sustainable innovation. Waltcorp’s Life Sciences Consulting division is committed to helping organizations design and implement tailored regulatory strategies that balance compliance with breakthrough innovation.