Introduction
Recruitment is one of the most resource-intensive business functions, with organizations spending an average of $4,700 per hire and taking approximately 42 days to fill a position, according to the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM). The rise of AI promises to streamline this process by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing the accuracy of candidate selection, and reducing hiring costs. Companies are increasingly turning to AI-powered platforms such as LinkedIn, Workday, and HireVue to manage large volumes of applicants and identify the best-fit candidates more efficiently.
However, AI’s growing role in recruitment raises critical questions about fairness, bias, and the human element in hiring decisions. While AI can enhance efficiency and reduce human error, it also introduces risks related to algorithmic discrimination and candidate rejection based on flawed data models. This article examines both the benefits and challenges of AI in recruitment, using real-world examples and market data to provide a balanced perspective.
The Good: How AI is Improving Recruitment
1. Faster Screening and Shortlisting
AI-driven applicant tracking systems (ATS) can analyze and screen thousands of resumes in seconds. Tools like HireVue and Pymetrics use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) to match resumes against job descriptions, identifying the most qualified candidates based on experience, skills, and education.
- Example:
Unilever implemented an AI-based recruitment platform to handle initial screening and assessments. The system reduced the hiring process by 75% and cut down hiring costs by 30% while improving the diversity of shortlisted candidates.
2. Bias Reduction and Objective Decision-Making
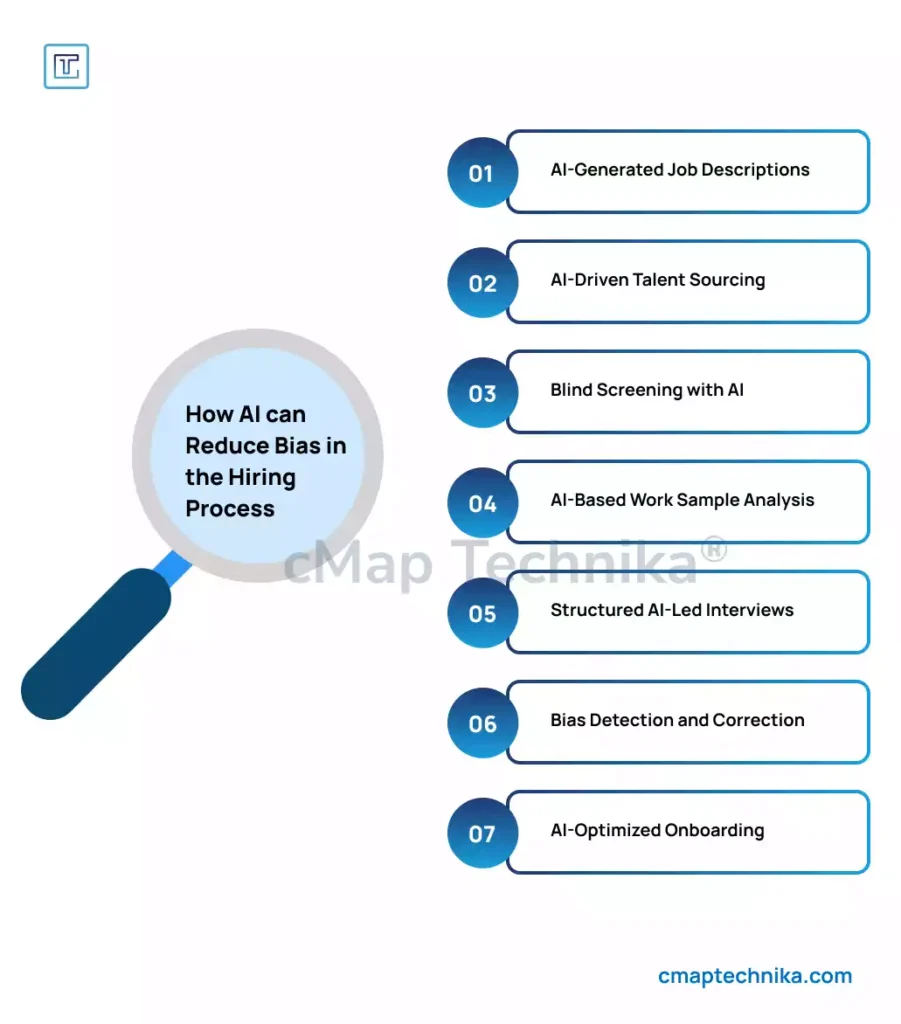
AI can help reduce unconscious bias by focusing on objective criteria such as skills and qualifications rather than gender, ethnicity, or age. Algorithms trained on diverse datasets can identify top candidates based purely on their competency rather than subjective factors.
- Example:
IBM’s AI-powered recruitment platform increased diversity in the hiring process by analyzing patterns in hiring data and suggesting improvements to reduce biases. The tool resulted in a 12% increase in diverse hiring.
3. Enhanced Candidate Experience
AI chatbots and virtual assistants provide immediate responses to candidate inquiries, schedule interviews, and offer feedback. This improves the candidate experience by reducing wait times and ensuring better communication throughout the process.
- Example:
L’Oréal implemented an AI-driven chatbot that handles over 10,000 candidate interactions per month. It answers FAQs, schedules interviews, and provides real-time updates on application status, increasing candidate satisfaction scores by 35%.
4. Predictive Analytics for Better Hiring Decisions
AI tools analyze historical hiring data and employee performance to predict which candidates are likely to succeed. Machine learning models can identify patterns in successful hires and recommend candidates with similar traits.
- Example:
Google’s AI-powered hiring platform increased employee retention rates by 22% by using predictive analytics to match candidates with the right teams and roles based on behavioral data and career history.
The Bad: Challenges and Risks of AI in Recruitment
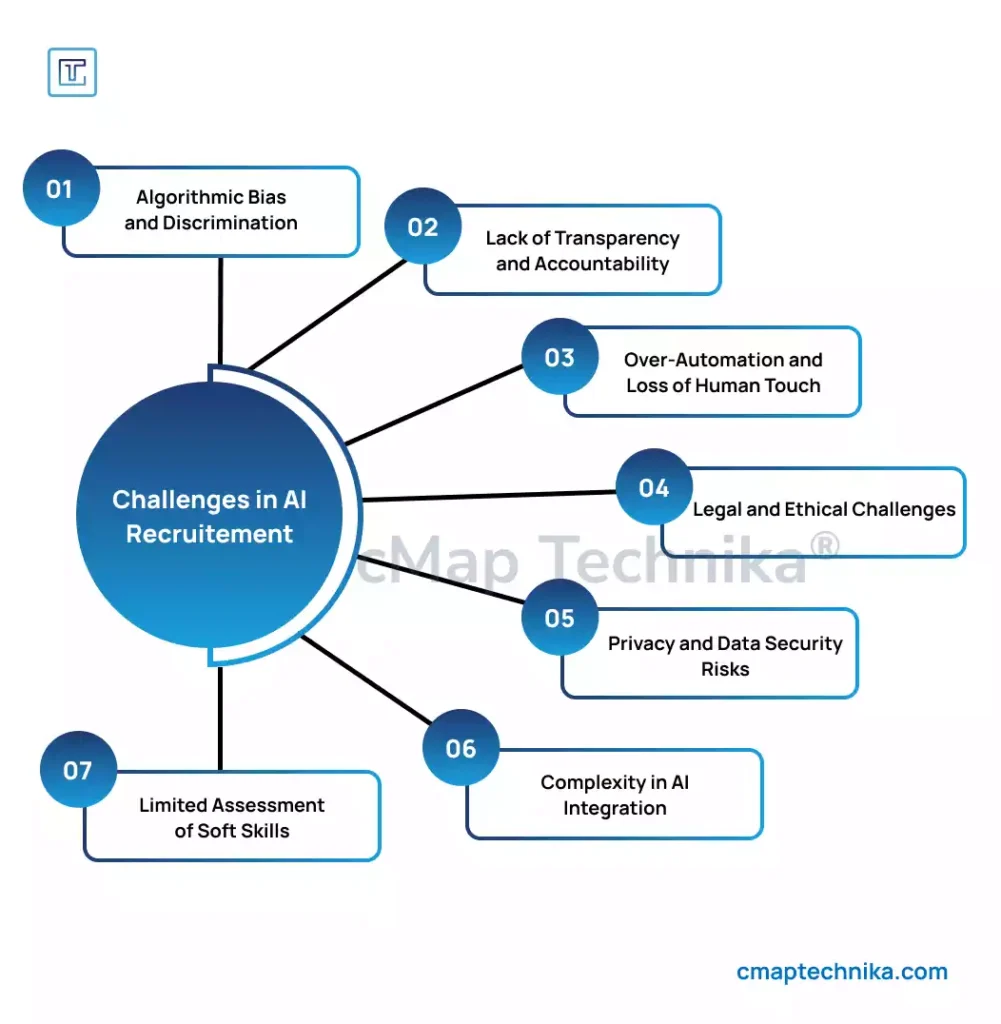
1. Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination
AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. If historical hiring data reflects existing biases (e.g., gender, ethnicity), the AI model will likely perpetuate these patterns. Amazon’s AI recruitment tool was scrapped after it was found to favor male candidates due to historical male dominance in tech roles.
- Example:
A 2018 study showed that an AI recruitment tool rejected resumes with the word “women’s” (e.g., “women’s chess club”) because historical data favored male applicants.
2. Lack of Transparency and Accountability
AI systems often operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult for recruiters to understand why certain candidates were selected or rejected. This lack of transparency can lead to distrust and legal challenges.
- Example:
A healthcare company using an AI-driven recruitment tool faced backlash after candidates with strong qualifications were repeatedly rejected. An audit revealed that the algorithm had learned to penalize candidates with employment gaps — even those due to maternity leave.
3. Over-Automation and Loss of Human Touch
While AI can automate the screening and assessment process, it lacks the human ability to assess soft skills, emotional intelligence, and cultural fit. Over-reliance on AI can make the hiring process impersonal and discourage top talent.
- Example:
A leading consulting firm reported a 17% decline in candidate acceptance rates after automating the initial screening process, suggesting that lack of human interaction contributed to reduced engagement.
4. Legal and Ethical Concerns
AI recruitment platforms must comply with labor laws, data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR), and anti-discrimination guidelines. Companies face potential legal exposure if AI-driven hiring processes inadvertently lead to discriminatory outcomes.
- Example:
In 2021, the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) launched an investigation into several AI-based recruitment platforms for potentially violating hiring fairness regulations.
The Reality: Where AI in Recruitment Stands Today
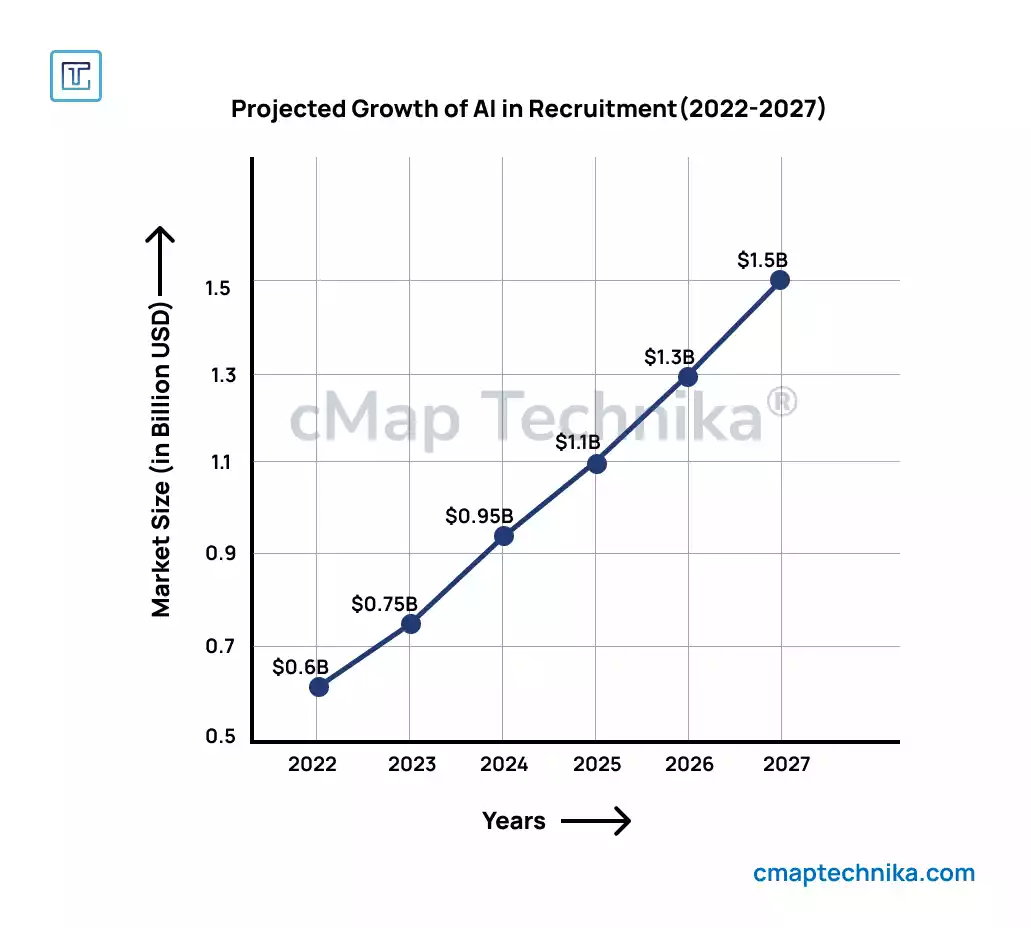
Despite its challenges, AI-driven recruitment is rapidly expanding. According to a report by Gartner, over 75% of large enterprises now use AI-based recruitment tools, and this figure is expected to grow. The AI recruitment market is valued at approximately $600 million and is projected to reach $1.5 billion by 2027.
Key Industry Trends:
- AI-Powered Video Interviews: Tools like HireVue and Modern Hire analyze facial expressions, tone, and speech patterns to assess candidate suitability.
- Skills-Based Hiring: Companies are shifting toward AI-driven skills-based assessments rather than focusing solely on education and experience.
- Internal Talent Mobility: AI helps identify existing employees suitable for internal promotions and lateral moves, enhancing employee retention.
Case Study: AI-Driven Recruitment Success at Hilton
Hilton introduced an AI-based recruitment platform to handle high application volumes for entry-level positions. The platform automated resume screening, scheduled interviews, and assessed candidate communication skills using natural language processing.
- Reduced hiring time by 40%
- Increased candidate quality by 27%
- Reduced hiring costs by 30%
Conclusion and Recommendations
AI has the potential to revolutionize recruitment by enhancing efficiency, improving candidate matching, and reducing hiring costs. However, the risks associated with bias, over-automation, and lack of transparency require careful management. Organizations must:
- Regularly audit AI algorithms to identify and mitigate bias.
- Maintain a human element in the hiring process to assess soft skills and cultural fit.
- Ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards to avoid reputational and legal risks.
- Educate recruiters and HR professionals on the capabilities and limitations of AI tools.
AI will continue to shape the future of recruitment — but the key to success lies in balancing automation with human oversight to create a fair, transparent, and effective hiring process.






