Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a futuristic concept—it is a powerful force reshaping the business world at an unprecedented pace. From automating repetitive tasks to unlocking new frontiers of innovation, AI is revolutionizing how companies operate, compete, and grow. Businesses that once relied on traditional models are now leveraging AI to optimize efficiency, enhance decision-making, and uncover untapped market potential. Beyond mere automation, AI-driven solutions are enabling smarter strategies, predictive analytics, and hyper-personalized customer experiences, redefining industries in the process. As organizations race to integrate AI into their core operations, those that harness its full potential will not only gain a competitive edge but also shape the future of commerce itself. This white paper explores the transformative impact of AI, illustrating how it is not just streamlining workflows but also driving innovation that redefines the very nature of business.
The Evolution of AI in Business
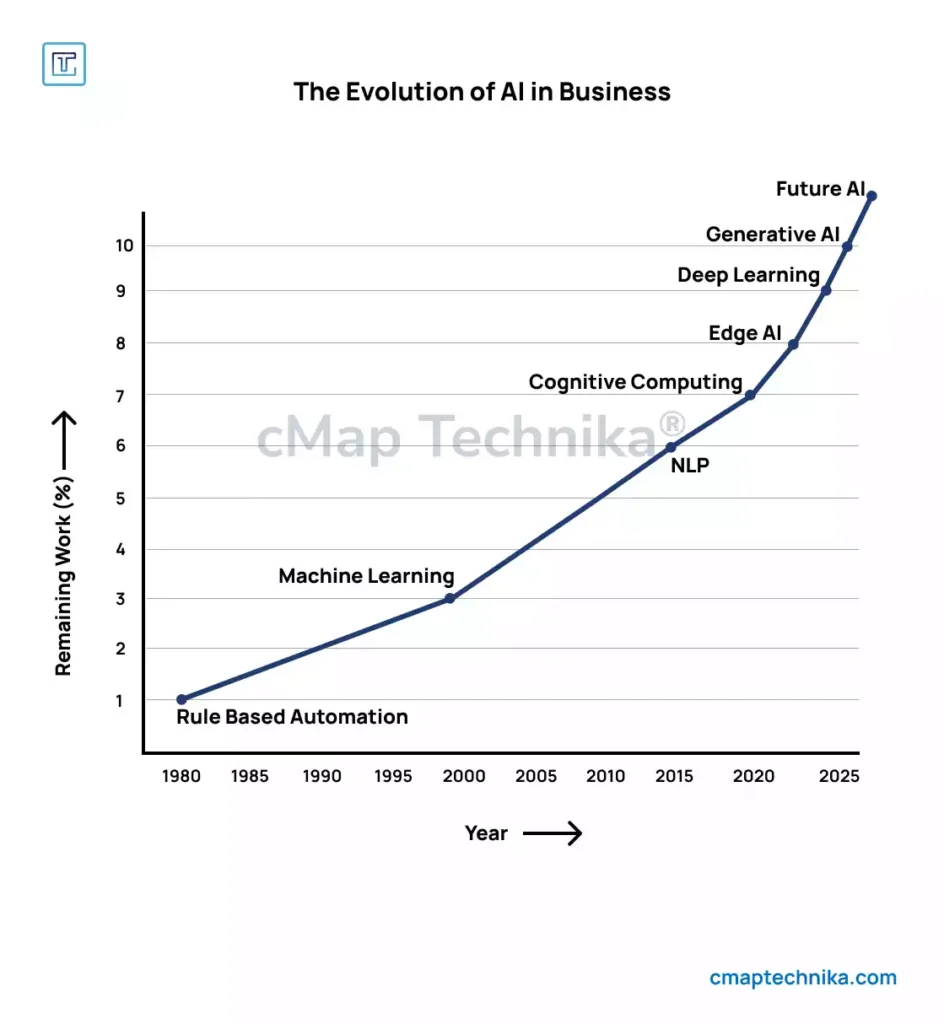
AI’s integration into business began with basic rule-based automation, where structured algorithms followed predefined instructions to streamline repetitive tasks. Over time, AI has evolved into a powerful force, leveraging machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing (NLP) to perform complex cognitive functions once thought to be exclusive to human intelligence. Today, AI is deeply embedded across industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, driving efficiency, insights, and innovation.
The journey of AI in business can be traced through several key milestones. The early adoption of robotic process automation (RPA) revolutionized back-office operations, automating mundane, rule-based tasks and reducing human error. As machine learning and NLP advanced, businesses gained the ability to analyze vast datasets, extract meaningful insights, and enhance customer interactions with intelligent chatbots and recommendation systems. The latest wave of AI evolution, marked by generative AI and deep learning, has gone beyond mere automation—businesses can now create hyper-personalized experiences, predict market trends with unprecedented accuracy, and even generate content, designs, and code autonomously. This transformation underscores AI’s shift from being a tool for efficiency to a driver of innovation, opening new frontiers in business strategy and competitive advantage.
AI in Business Automation
Automation remains one of AI’s most impactful contributions to business. By leveraging AI-powered automation, organizations streamline workflows and improve efficiency.
Key Areas of Automation:
- Customer Service: AI chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 support, reducing response times and operational costs.
- Supply Chain Management: Predictive analytics optimize inventory management and logistics, reducing waste and enhancing efficiency.
- Finance and Accounting: AI automates fraud detection, expense tracking, and risk assessment, increasing accuracy and security.
- Human Resources: AI-driven tools enhance recruitment, onboarding, and employee engagement through data-driven insights.
AI as a Driver of Business Innovation
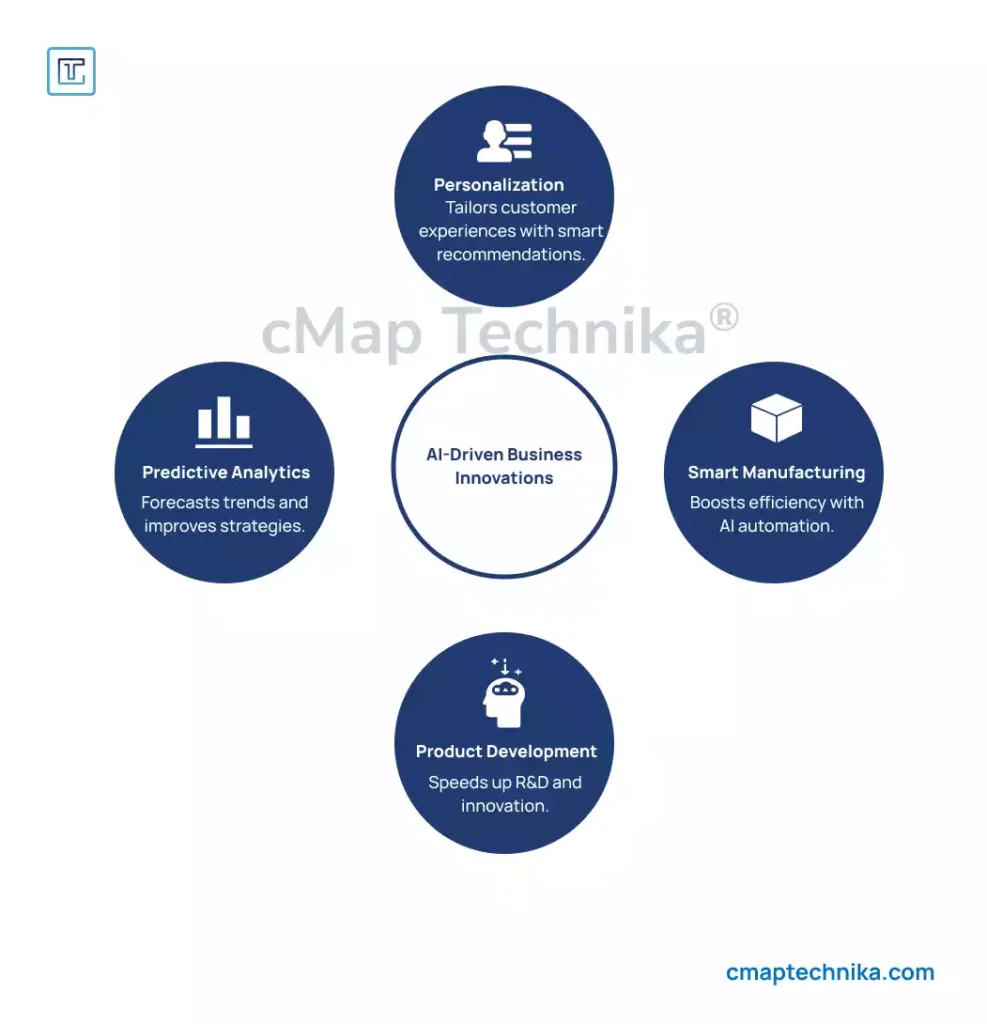
Beyond automation, AI fuels business transformation by enabling new business models and improving decision-making.
AI-Driven Innovations:
- Personalization: AI-powered recommendation engines enhance customer experiences by delivering tailored content and product suggestions.
- Predictive Analytics: Businesses use AI to forecast market trends, optimize pricing strategies, and anticipate consumer demand.
- Product Development: AI accelerates research and development, fostering innovation in pharmaceuticals, engineering, and software development.
- Smart Manufacturing: AI-powered robotics and IoT integration enhance precision, reduce downtime, and optimize production processes.
Case Study 1: AI in Retail – Amazon’s Personalization Engine
Amazon, one of the world’s largest e-commerce companies, has set the gold standard for AI-powered recommendation systems. Its proprietary algorithm analyzes customer browsing history, past purchases, and real-time behavior to deliver personalized product recommendations. This AI-driven approach has significantly improved customer engagement, increased average order value, and enhanced sales conversions. According to a report by McKinsey, Amazon’s recommendation engine is responsible for nearly 35% of its total sales. The AI model continuously refines its predictions by incorporating user feedback, seasonal trends, and emerging market preferences, creating a dynamic and ever-evolving customer experience.
Case Study 2: AI in Healthcare – Detecting Diseases with IBM Watson Health
IBM Watson Health has revolutionized medical diagnostics by leveraging AI to assist doctors in detecting diseases with greater accuracy. One notable application is in oncology, where Watson’s AI-driven system analyzes millions of medical papers, clinical trial results, and patient records to recommend personalized cancer treatment plans. In partnership with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, Watson Health has successfully assisted oncologists in identifying optimal treatment options based on genetic markers and patient history. In another instance, Google’s DeepMind developed an AI system that detects over 50 eye diseases with accuracy comparable to leading ophthalmologists. These AI models not only speed up diagnosis but also reduce human error, ensuring better patient outcomes.
Case Study 3: AI in Finance – JPMorgan Chase’s AI Fraud Detection
JPMorgan Chase, one of the largest financial institutions, has implemented an advanced AI-powered fraud detection system to combat financial crimes. The AI model analyzes millions of transactions in real time, identifying patterns that indicate potential fraudulent activity. By leveraging machine learning, the system adapts to evolving cyber threats and recognizes anomalies that traditional rule-based detection methods would miss. As a result, JPMorgan has significantly reduced fraudulent transactions and enhanced its cybersecurity infrastructure. Additionally, AI-powered robo-advisors such as those used by Wealthfront and Betterment provide personalized financial planning based on user behavior, risk tolerance, and market trends, democratizing investment opportunities for a broader audience.
These case studies highlight how AI is not just an automation tool but a strategic enabler of innovation across industries. Whether in retail, healthcare, or finance, AI continues to reshape business landscapes, driving efficiency, security, and customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
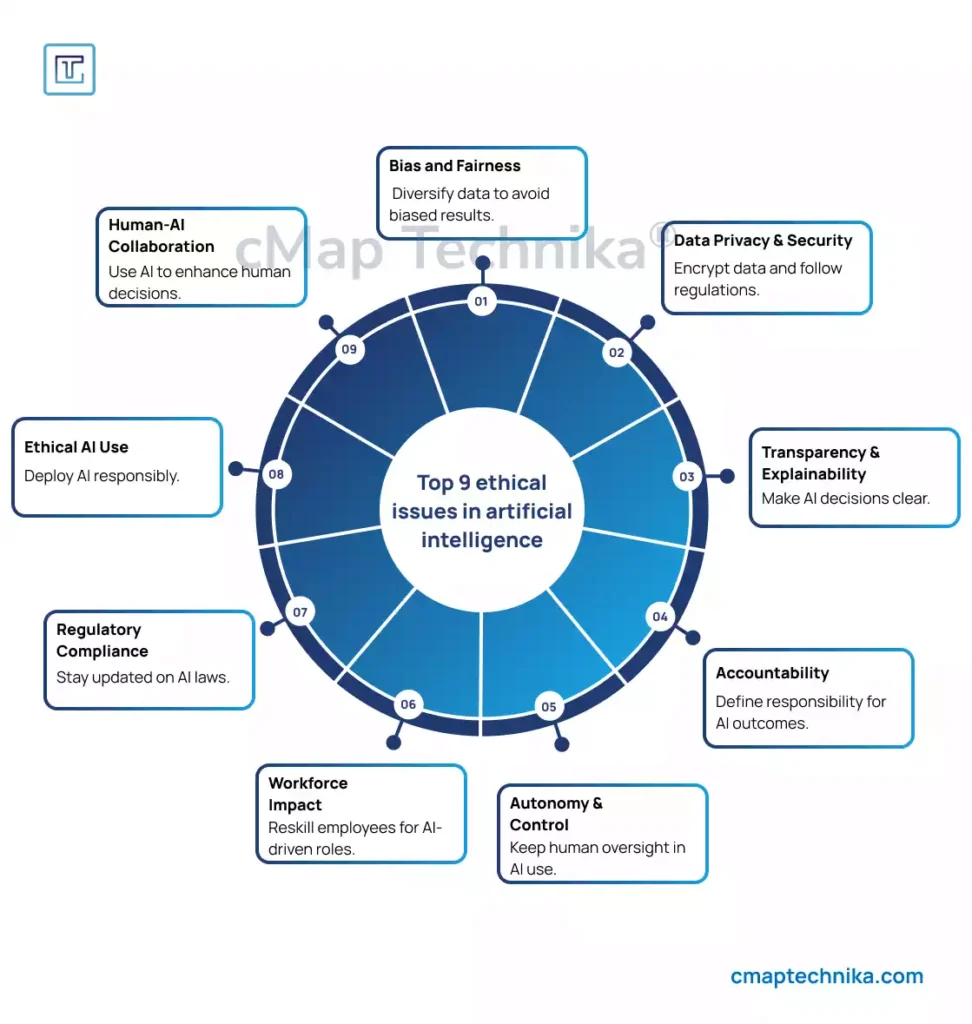
While AI holds immense potential to drive innovation and efficiency, businesses must carefully address several critical challenges and ethical considerations to ensure responsible deployment and sustainable growth. Mismanagement of these factors can lead to reputational damage, legal consequences, and diminished customer trust.
1. Bias and Fairness
AI models are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. If training data reflects existing social or economic biases, the AI system can amplify these issues, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Example: In 2018, Amazon’s AI recruiting tool was discovered to have gender bias, penalizing resumes that contained the word “women” or referenced women’s organizations. This happened because the model was trained on historical hiring data, which favored male applicants. As a result, the model systematically filtered out qualified female candidates, highlighting how deeply embedded biases in training data can affect AI-driven decisions.
- Example: Facial recognition technology has been shown to have higher error rates for individuals with darker skin tones. A 2019 study by MIT showed that commercial facial recognition systems had an error rate of nearly 35% for darker-skinned women, compared to less than 1% for lighter-skinned men. This disparity stems from training data that underrepresents certain demographic groups.
To address these issues, businesses need to diversify training data, implement algorithmic fairness techniques, and conduct bias audits regularly. Techniques like adversarial debiasing, which trains models to minimize bias, and explainable AI (XAI), which provides transparency into decision-making, can help mitigate bias risks.
2. Data Privacy and Security
AI systems rely on large volumes of personal and business data to function effectively. This includes customer profiles, transaction history, and real-time behavioral data. The more sensitive the data, the higher the risk of breaches or misuse. Mishandling such data can lead to financial penalties, reputational damage, and regulatory scrutiny.
- Example: In 2021, Facebook experienced a data breach where personal data of over 530 million users, including phone numbers and email addresses, was leaked. This breach exposed vulnerabilities in data handling practices and raised concerns about how AI systems access and store user information.
- Example: In healthcare, AI models trained on patient data face strict compliance requirements under regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). An AI-driven diagnostic tool was found to have improperly stored patient records on a third-party cloud, violating data privacy standards and resulting in legal action.
Companies must implement strict data encryption protocols, anonymize sensitive data, and establish governance frameworks to control how AI models access and store data. Ensuring compliance with regulations such as the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is crucial for maintaining customer trust.
3. Workforce Displacement and Transformation
AI-driven automation is expected to replace certain roles, particularly those involving repetitive or manual tasks. However, AI also creates new opportunities, particularly in AI development, data analysis, and system maintenance.
- Example: In manufacturing, automotive companies like Tesla and Toyota have automated assembly lines using AI-driven robotic systems. While this has reduced the need for line workers, it has simultaneously increased the demand for AI engineers, system maintenance specialists, and software developers.
- Example: In the financial sector, AI-based customer service chatbots have reduced the need for human agents in handling routine inquiries. However, this shift has led to the creation of new roles focused on training, improving, and overseeing chatbot performance.
To mitigate workforce displacement, businesses should invest in reskilling and upskilling programs. AI can be leveraged to design personalized training programs that help employees transition into new roles aligned with evolving business needs.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Responsibility
AI regulations are evolving rapidly as governments seek to balance innovation with consumer protection and ethical responsibility. Businesses operating AI models must navigate a complex and frequently changing regulatory landscape.
- Example: The European Union’s proposed AI Act aims to regulate AI systems based on their risk levels. High-risk AI applications, such as biometric surveillance and credit scoring, will require detailed documentation, transparency, and regular oversight.
- Example: China’s AI regulatory framework includes strict guidelines on algorithmic transparency and content moderation, particularly for AI-driven social media platforms. In 2022, several Chinese companies faced fines for failing to comply with AI content standards.
Businesses should establish internal AI governance frameworks, appoint AI ethics officers, and collaborate with policymakers to anticipate and adapt to regulatory changes. Developing transparent AI models and providing clear explanations for AI-driven decisions will be critical to maintaining compliance and customer trust.
The Future of AI in Business
AI’s role in business will continue to expand, driven by advancements in machine learning, deep learning, and human-AI collaboration. Businesses that anticipate and adapt to these advancements will gain a competitive edge and unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation.
1. AI-Powered Autonomous Systems
AI-driven autonomous systems are poised to transform industries by increasing efficiency, reducing human error, and enabling new business models.
- Example: Tesla’s Autopilot system processes real-time data from cameras, radar, and ultrasonic sensors to enable self-driving capabilities. The system continuously improves through machine learning, adjusting to road conditions and driver behavior.
- Example: Amazon’s automated warehouses use AI-guided robots to pick, pack, and sort inventory. These systems optimize routes and inventory placement to maximize speed and reduce labor costs.
- Example: In healthcare, AI-powered surgical robots are assisting surgeons in complex procedures with greater precision and minimal invasiveness. Companies like Intuitive Surgical have developed AI-driven robotic systems that enhance the accuracy and safety of medical procedures.
2. Explainable AI (XAI)
One of the key barriers to AI adoption is the “black box” nature of complex models, where decision-making processes are not transparent. Explainable AI (XAI) aims to provide clear, interpretable insights into how AI models reach conclusions.
- Example: Healthcare companies are using XAI to explain AI-generated diagnostic recommendations to doctors. IBM’s Watson Health, for instance, provides a breakdown of the clinical studies and patient data that influenced its diagnosis.
- Example: Financial institutions use XAI to explain credit decisions to customers. Instead of issuing an automated rejection, the system provides detailed reasoning, such as credit history, debt-to-income ratio, and repayment patterns.
XAI builds trust with customers and regulators while helping businesses identify weaknesses and improve model performance.
3. AI-Augmented Workforce
AI is not just replacing human workers—it is augmenting them by enhancing productivity and creativity. AI tools can automate repetitive tasks, analyze large datasets, and generate insights, freeing up human workers for higher-value activities.
- Example: Microsoft’s GitHub Copilot assists software developers by suggesting code completions and identifying bugs in real time, improving development speed and code quality.
- Example: AI-driven CRM platforms like Salesforce’s Einstein automate customer outreach and lead qualification, allowing sales teams to focus on closing deals and building relationships.
AI-augmented roles will become the norm across industries. Businesses that leverage AI to enhance rather than replace human work will see higher productivity and employee satisfaction.
4. Sustainable AI Solutions
AI can help businesses meet sustainability goals by optimizing resource consumption, reducing waste, and improving energy efficiency.
- Example: Google’s AI-driven cooling system reduced energy consumption in its data centers by 40% by dynamically adjusting cooling based on real-time temperature and humidity data.
- Example: AI-based supply chain platforms are helping companies reduce waste and improve inventory management by predicting demand more accurately and adjusting procurement cycles accordingly.
AI-driven sustainability initiatives will become critical as businesses face increasing pressure from stakeholders and regulators to minimize environmental impact. Sustainable AI solutions will also enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Conclusion
AI is reshaping business landscapes, evolving from a tool for automation into a catalyst for innovation. By embracing AI responsibly and strategically, businesses can unlock new opportunities, enhance customer experiences, and maintain a competitive edge in the digital era. While challenges remain, the future of AI in business is undeniably promising, paving the way for a more efficient, innovative, and intelligent world.






