Introduction
The rapid evolution of software development has compelled organizations to seek more efficient, reliable, and scalable approaches to delivering software. In this context, DevOps—an integrated approach combining development and operations—has emerged as a game-changer. At the heart of DevOps’ success lies automation. Automation in DevOps enables faster release cycles, higher-quality software, and reduced operational costs. As businesses increasingly adopt cloud-native environments and microservices architectures, the role of automation in DevOps has become more critical than ever. This research report explores how automation is transforming DevOps processes, examines the key challenges and benefits, and provides real-world case studies of successful implementations.
The Role of Automation in DevOps

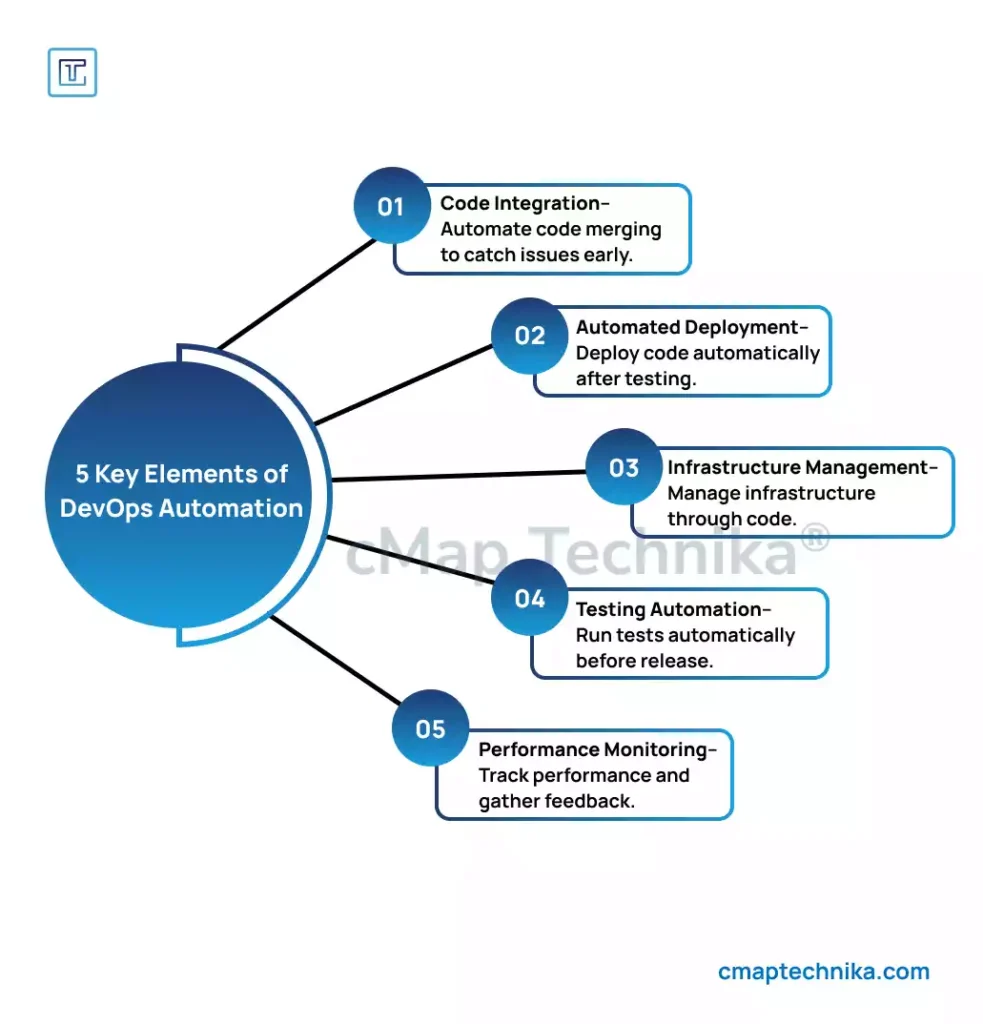
Automation in DevOps refers to the systematic use of tools and scripts to streamline and accelerate the entire software delivery lifecycle (SDLC). It encompasses a wide range of activities, including code integration, testing, deployment, monitoring, and infrastructure provisioning. The goal is to reduce manual effort, minimize human error, and enable continuous improvement through faster feedback loops.
Traditionally, software development and operations teams operated in silos, leading to communication gaps, slower deployment cycles, and inconsistent software quality. DevOps bridges this gap by fostering a collaborative environment where development and operations teams work together toward a shared goal. Automation is the catalyst that makes this collaboration seamless and efficient.
For example, continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines automate code building, testing, and deployment. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) allows developers to define infrastructure requirements using code, enabling consistent and repeatable deployments across different environments. Automated monitoring tools provide real-time insights into system performance, allowing teams to detect and resolve issues proactively.
Key Benefits of Automation in DevOps
1. Faster Time to Market
Automation significantly reduces the time required to develop, test, and deploy software. CI/CD pipelines automate the process of integrating code changes and delivering them to production, shortening release cycles from weeks to hours. Faster delivery enables businesses to respond more swiftly to market demands and customer feedback.
A survey by Puppet found that high-performing DevOps teams deploy code 46 times more frequently and recover from failures 96 times faster than low-performing teams. Automated deployment pipelines eliminate bottlenecks and allow teams to release new features and fixes more frequently, enhancing business agility.
2. Improved Code Quality and Consistency
Manual code integration and testing are prone to human error, leading to inconsistent software quality. Automation ensures that code is consistently tested and validated against predefined criteria before being released. Tools like Selenium and Jenkins enable automated testing at various stages of the development cycle, reducing the risk of bugs and regressions.
Automated linting tools and code analyzers ensure that coding standards are maintained across the development team. Automated deployment scripts minimize the chances of configuration drift and environmental inconsistencies, leading to more reliable software releases.
3. Cost Efficiency
Automation reduces the need for manual intervention, which translates into lower labor costs and fewer operational disruptions. Automated infrastructure provisioning eliminates the need for dedicated infrastructure management teams, allowing organizations to scale resources dynamically based on demand.
Additionally, automated monitoring and logging tools help identify performance issues and resource wastage, enabling cost optimization. A report by Forrester estimates that companies adopting DevOps automation can reduce operational costs by up to 30%.
4. Enhanced Security and Compliance
Security is a growing concern in software development, particularly in cloud-based environments. Automation helps embed security checks into the development pipeline, ensuring that vulnerabilities are detected and mitigated early. Tools like HashiCorp Vault and SonarQube automate security scans and secret management, enhancing overall system security.
Automated compliance audits ensure that software deployments adhere to industry regulations and internal security standards. By automating compliance reporting, organizations can reduce the risk of regulatory fines and improve their security posture.
Challenges in Implementing Automation in DevOps
1. Skills Gap and Talent Acquisition
The growing complexity of DevOps tools and frameworks has created a significant skills gap. Organizations struggle to find qualified DevOps engineers with expertise in automation tools, cloud platforms, and containerization technologies.
Companies that fail to invest in training and upskilling face longer implementation timelines and higher failure rates. Successful DevOps adoption requires a combination of technical proficiency and cultural alignment.
2. Complexity of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Many organizations operate in multi-cloud and hybrid environments, which complicates automation efforts. Each cloud provider has unique APIs, security configurations, and deployment models. Developing a consistent automation strategy across multiple environments requires careful planning and robust tooling.
3. Resistance to Change
Shifting to an automated DevOps model requires a cultural transformation. Traditional development and operations teams may resist automation due to concerns about job security and loss of control. Overcoming this resistance requires strong leadership, clear communication, and demonstrated benefits from automation initiatives.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Netflix – Pioneering DevOps Automation
Netflix is a prime example of how automation can drive operational efficiency and scalability. With over 230 million subscribers worldwide, Netflix must manage massive traffic volumes and deliver a seamless streaming experience.
Netflix’s infrastructure is fully automated, from code deployment to scaling. The company’s Simian Army—a suite of automation tools—tests the resilience of its infrastructure by simulating failures and unexpected events.
- Chaos Monkey randomly shuts down instances to test fault tolerance.
- Conformity Monkey detects and removes misconfigured instances.
- Latency Monkey introduces artificial latency to test system responsiveness.
By automating failure recovery and performance testing, Netflix ensures that its platform remains stable and responsive, even under heavy load. This proactive approach to automation has enabled Netflix to maintain high availability and deliver new features quickly.
Case Study 2: Capital One – Scaling DevOps with Infrastructure as Code
Capital One, a leading financial institution, adopted DevOps automation to accelerate software delivery and improve regulatory compliance. The company transitioned from a monolithic architecture to microservices, enabling more agile development cycles.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) using Terraform and AWS CloudFormation allowed Capital One to standardize infrastructure deployment across its cloud environments. Automated security scans using SonarQube and Aqua ensured that code met security standards before deployment.
By automating infrastructure provisioning and security testing, Capital One reduced deployment times from days to minutes, improved compliance reporting, and enhanced overall system security.
Case Study 3: Etsy – Continuous Deployment at Scale
Etsy, an e-commerce platform, implemented a fully automated CI/CD pipeline to support its fast-growing user base. Engineers at Etsy deploy code more than 50 times a day without causing service disruptions.
Key automation tools include:
- Jenkins for automated builds and tests.
- Docker for containerized deployments.
- Prometheus for real-time monitoring and alerting.
Automated feature flags allow Etsy to deploy new features incrementally, reducing the risk of failure. If an issue arises, the feature can be rolled back automatically without affecting other parts of the system.
Future Trends in DevOps Automation
The future of DevOps automation lies in AI and machine learning. Predictive analytics can identify potential performance bottlenecks before they occur, allowing teams to address them proactively.
AI-driven test automation enables more sophisticated test scenarios and higher test coverage. Self-healing systems that automatically detect and resolve issues without human intervention are becoming a reality.
Hyper-automation, which combines AI, machine learning, and RPA, is expected to redefine DevOps. Automated governance and policy enforcement will ensure that deployments meet compliance standards without manual oversight.
Conclusion
Automation is the driving force behind DevOps transformation. By reducing manual effort, increasing release velocity, and improving software quality, automation enables organizations to stay competitive in an increasingly dynamic market. Case studies from Netflix, Capital One, and Etsy demonstrate how automation can scale DevOps processes and drive operational efficiency. As AI and machine learning continue to evolve, the future of DevOps automation promises even greater efficiency, resilience, and innovation. For businesses seeking to thrive in the digital age, embracing DevOps automation is no longer optional—it’s essential.






