In today’s fast-paced, information-rich world, data has become a valuable commodity in nearly every industry, and education is no exception. The increasing integration of technology in the classroom has made it easier to collect vast amounts of data about student performance, learning behaviors, and institutional effectiveness. By harnessing the power of data analytics, educational institutions can make more informed decisions, tailor interventions, and optimize the learning experience to improve student outcomes. This article delves into how data-driven decision-making is transforming education, enhancing student performance, and driving systemic improvements across schools and universities.
The Role of Data Analytics in Education
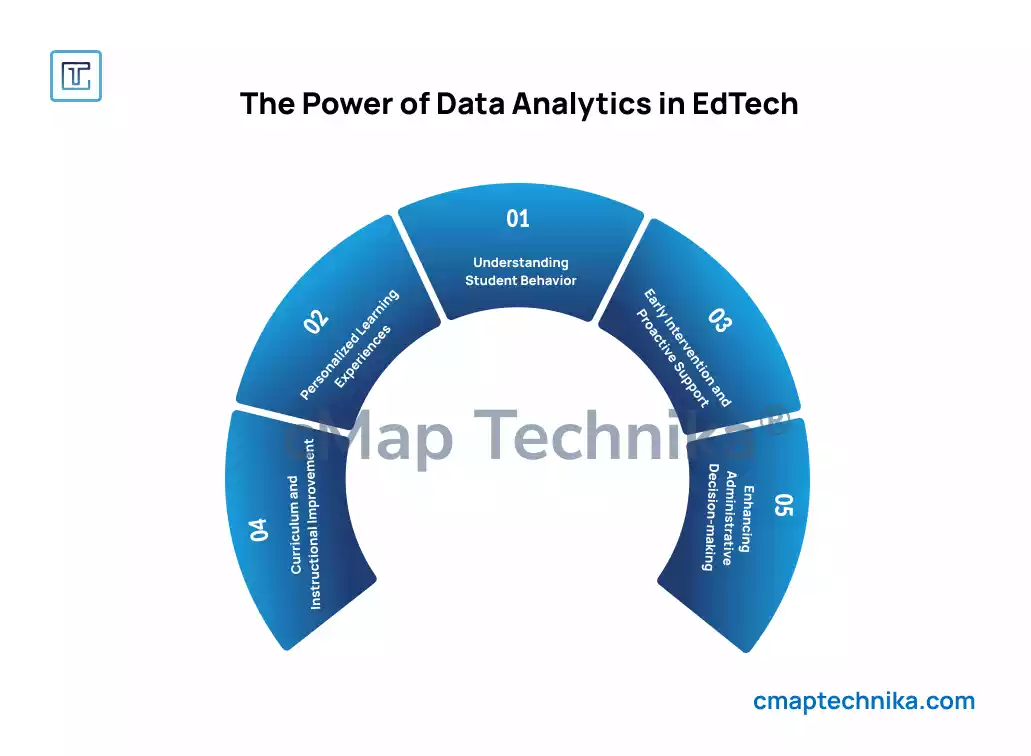
Data analytics in education involves collecting, analyzing, and using data to inform decisions and improve learning outcomes. This data can come from a variety of sources, including student assessments, classroom participation, attendance records, learning management systems (LMS), and more. The insights derived from this data can help educators and administrators identify trends, spot potential issues early, and take proactive steps to address challenges before they escalate.
In the past, educational decision-making often relied on intuition and anecdotal evidence. However, the shift towards data-driven decision-making allows schools, teachers, and policymakers to make decisions based on empirical evidence and insights, ensuring a more objective, informed approach to education. By understanding how students are progressing and where they may be struggling, educators can customize their strategies to meet the specific needs of individual learners.
Key Areas Where Data Analytics Is Making an Impact
1. Tracking Student Performance
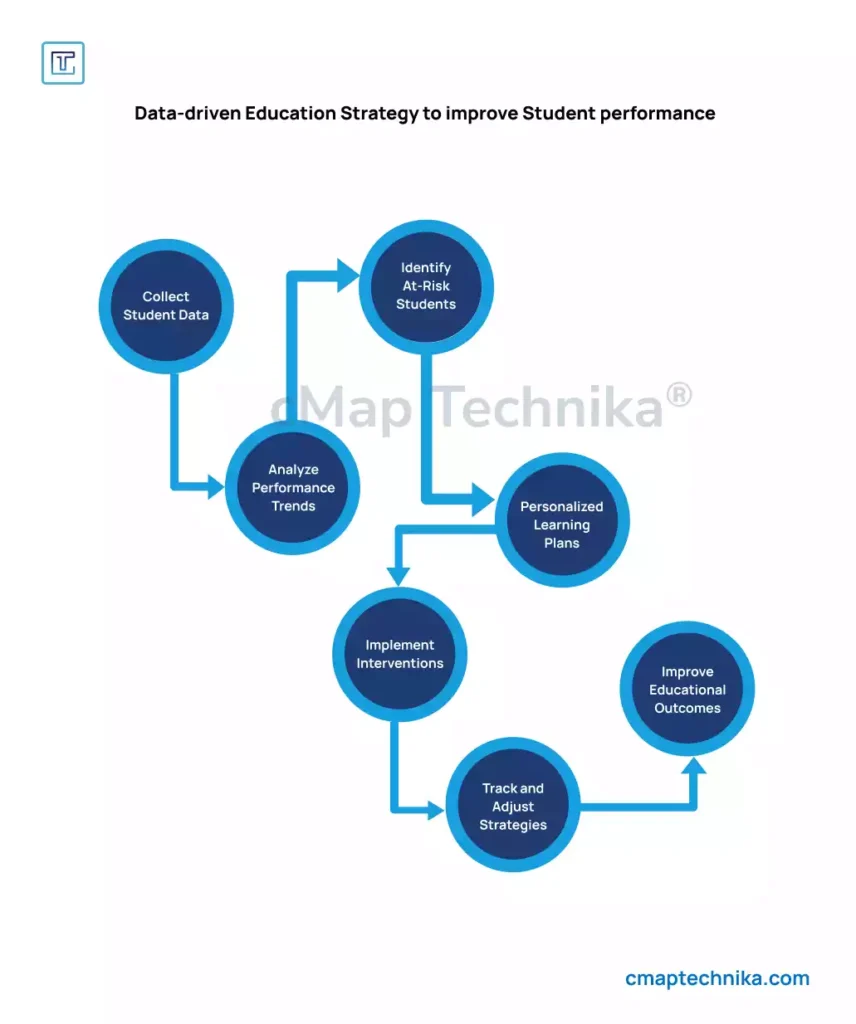
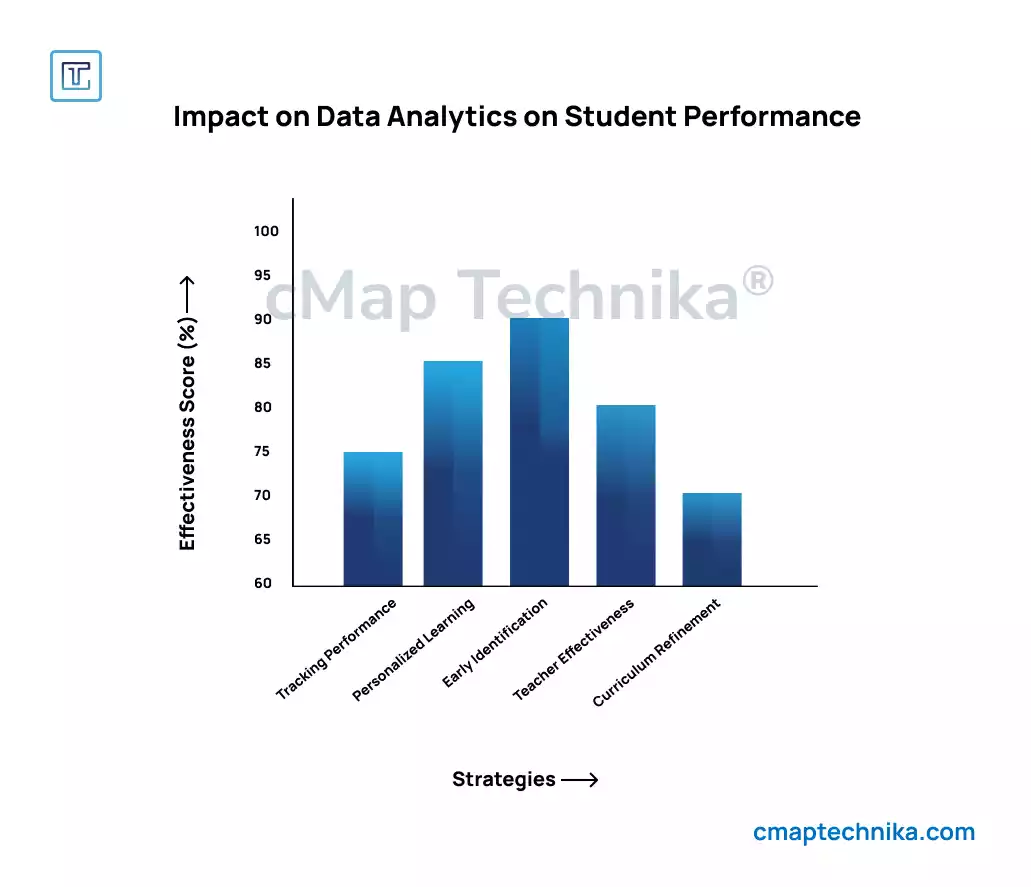
One of the most immediate and impactful uses of data analytics in education is tracking student performance. Traditionally, assessment data (tests, assignments, quizzes) was stored in isolated records, making it difficult to track trends or get a holistic view of a student’s academic progress. With the advent of digital learning platforms, it is now possible to track performance in real time and over extended periods, providing a clearer picture of how students are progressing.
Learning management systems like Canvas, Blackboard, and Google Classroom allow teachers to track how students engage with learning materials, participate in discussions, and perform on assessments. This data can then be used to:
- Identify patterns in performance across different subjects and assessments.
- Monitor individual student progress over time.
- Recognize at-risk students early on who may need additional support or intervention.
- Determine which teaching methods and materials are most effective for different types of learners.
By continuously monitoring and analyzing student performance data, educators can quickly adapt their instructional strategies to address gaps in knowledge and ensure students stay on track to meet learning objectives.
2. Personalized Learning
Data analytics is a critical enabler of personalized learning, where instruction is tailored to meet the unique needs of each student. Traditional classroom settings often require students to follow the same pace and curriculum, regardless of their individual learning styles or abilities. Data-driven tools, however, provide teachers with the insights needed to offer personalized instruction that suits the varying levels, strengths, and challenges of their students.
For example, adaptive learning platforms use data to adjust the difficulty of lessons based on a student’s performance. If a student excels in a particular area, the platform can present more challenging material to keep them engaged. Conversely, if a student struggles with a concept, the system can offer additional practice, resources, and alternative explanations to help them grasp the material.
Tools such as DreamBox and Knewton analyze student responses, track patterns in learning behavior, and create personalized learning paths, ensuring that each student receives content that is appropriately challenging. This personalized approach can lead to better engagement, higher retention rates, and improved outcomes.
3. Early Identification of At-Risk Students
One of the most significant advantages of data analytics in education is its ability to identify at-risk students early. By continuously tracking various data points, educators can detect signs of disengagement, underperformance, or behavioral issues that might otherwise go unnoticed until it’s too late.
For example, data analytics platforms can highlight trends such as declining test scores, frequent absenteeism, or a lack of participation in online discussions. By identifying these early warning signs, teachers and administrators can intervene before students fall further behind, providing them with the necessary support, whether that’s through tutoring, mentoring, or adjusted teaching methods.
This proactive approach helps prevent academic failure, reduces dropout rates, and ensures that students receive the help they need to succeed.
4. Improving Teacher Effectiveness
Data analytics isn’t just beneficial for students; it can also be used to improve teacher effectiveness. By analyzing data on how students respond to different teaching methods, educators can refine their approaches to maximize engagement and learning outcomes.
For instance, data on student performance across different teaching modules can reveal which strategies work best for certain types of students. Teachers can then use this information to adjust their curriculum or delivery methods, ensuring that their instruction is as effective as possible.
Furthermore, platforms like Edgenuity and TeachBoost offer teachers the opportunity to track their own performance over time. By collecting feedback from students, monitoring classroom engagement, and reviewing assessment results, teachers can identify areas where they may need further professional development or where adjustments to their teaching style are needed.
5. Curriculum Development and Refinement
Data analytics also plays a critical role in curriculum development and refinement. Schools and universities can analyze student performance data to determine whether certain subjects or areas of study need to be adjusted or improved. For instance, if large groups of students consistently struggle with a particular topic, it may indicate that the curriculum is not sufficiently addressing the needs of the learners, or that the topic needs to be taught differently.
Similarly, analytics can help schools determine which courses are most engaging or effective in preparing students for the workforce. By examining graduation rates, job placement statistics, and student satisfaction, institutions can continually refine and enhance their curriculum to ensure that it remains relevant, engaging, and aligned with the needs of students and employers alike.
6. Optimizing Resource Allocation
Effective use of data can also help institutions optimize their resources. Educational leaders can analyze patterns in resource usage—such as which tools and materials are most frequently accessed—and allocate funding and resources more effectively. This may involve investing in technology that has been proven to enhance learning outcomes or adjusting class sizes to ensure that students receive the attention they need.
Data can also reveal trends in student interest, helping educational institutions plan for future course offerings and support services. By understanding what students are engaging with and where they are struggling, institutions can better allocate their resources to meet the evolving needs of the student body.
Overcoming Challenges in Data-Driven Decision Making
While the potential of data analytics in education is immense, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. These include:
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring that student data is securely stored and protected is a top priority. Schools must comply with regulations such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) to safeguard sensitive information.
- Data Overload: The sheer volume of data available can be overwhelming. It is crucial for educators and administrators to focus on the most relevant data points and use them strategically, rather than getting lost in a sea of numbers.
- Training Educators: Educators need proper training to interpret and use data effectively. Without the right skills and knowledge, data may not be used to its full potential.
- Equity and Access: Not all students have equal access to the tools and technologies that generate data. Schools must ensure that all students have access to the resources they need to succeed, regardless of socioeconomic status.
The Future of Data-Driven Education
As technology continues to advance, the role of data in education will only grow more important. The future of data-driven education will likely see even more sophisticated tools that can analyze a broader range of data, including emotional and behavioral data, to provide even more personalized and effective learning experiences.
Moreover, with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, educational systems will become even more responsive, able to adjust in real time to meet the needs of individual students. The ability to make data-driven decisions will empower educators to enhance the learning experience, foster student success, and ultimately improve educational outcomes on a large scale.
Conclusion
Data-driven decision-making is transforming education by enabling educators to track student performance, identify challenges early, and personalize learning experiences. With the help of data analytics, schools and universities can make more informed decisions that lead to improved educational outcomes, from personalized instruction to better resource allocation. As technology continues to evolve, the use of data in education will become even more sophisticated, ensuring that every student has the support they need to succeed. By embracing data-driven strategies, educational institutions can help shape a brighter future for students, educators, and the world of education itself.







