Introduction
In today’s digital economy, cloud migration is no longer just an IT initiative—it is a strategic imperative for organizations aiming to enhance agility, scalability, and cost efficiency. Moving from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud enables businesses to streamline operations, improve resilience, and foster innovation. However, a poorly planned migration can lead to data loss, security vulnerabilities, performance issues, and unexpected costs.
A successful cloud migration requires a structured approach, balancing technological, operational, and business considerations. This guide provides a step-by-step framework for enterprises to navigate their cloud journey effectively, covering everything from initial assessment and planning to execution and post-migration optimization. By adopting best practices, organizations can minimize risks, maximize value, and future-proof their digital infrastructure.
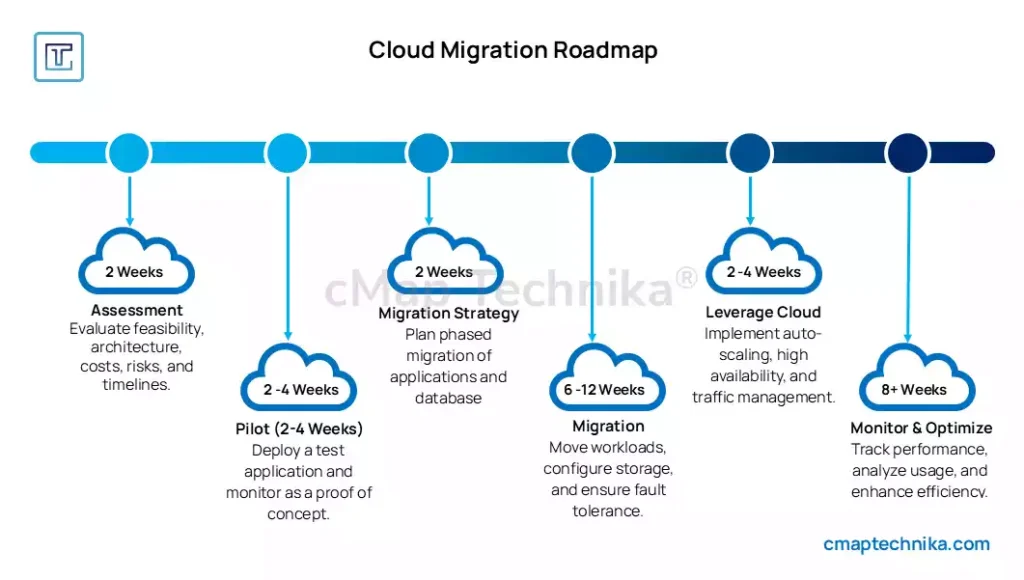
1. Assessing Readiness and Defining Objectives
Before embarking on cloud migration, organizations must take a step back and thoroughly evaluate their existing IT infrastructure, applications, and operational needs. A well-structured assessment helps mitigate risks, avoid costly missteps, and ensure a seamless transition to the cloud.
Key Steps:
- Conduct a Cloud Readiness Assessment – Evaluate your current infrastructure, application dependencies, and workloads to determine their compatibility with cloud environments. Identify legacy systems that may require reconfiguration or modernization.
- Define Clear Migration Objectives – Establish measurable goals, such as reducing IT costs, improving system reliability, enhancing security, or enabling faster innovation cycles. Align these objectives with business priorities to maximize ROI.
- Identify Potential Challenges – Assess risks such as compliance requirements, data residency laws, latency concerns, and potential service disruptions. Develop strategies to address these hurdles early in the process.
Organizations that invest time in thorough assessments lay a strong foundation for a smooth and efficient cloud migration, minimizing unexpected roadblocks down the line.
2. Choosing the Right Cloud Model and Provider
With multiple cloud deployment models and providers available, choosing the right fit is a crucial decision that impacts scalability, security, and long-term operational efficiency.
Key Considerations:
- Public Cloud (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, etc.) – Best suited for businesses that prioritize cost efficiency, scalability, and agility. Ideal for startups and enterprises looking for on-demand resources without heavy upfront investment.
- Private Cloud – Offers enhanced security, greater control, and compliance with strict regulations. Well-suited for industries such as healthcare and finance that handle sensitive data.
- Hybrid Cloud – Combines public and private cloud benefits, enabling flexibility and adherence to data sovereignty regulations. Organizations can keep critical workloads on-premises while leveraging public cloud for scalability.
Evaluating Cloud Providers:
When selecting a cloud provider, organizations should consider:
- Pricing structures and cost predictability – Evaluate on-demand vs. reserved pricing models.
- Compliance and security capabilities – Ensure adherence to industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs) – Assess provider guarantees for uptime, performance, and support.
Choosing the right model and provider ensures that organizations strike the perfect balance between cost efficiency, security, and performance.
3. Developing a Comprehensive Migration Strategy
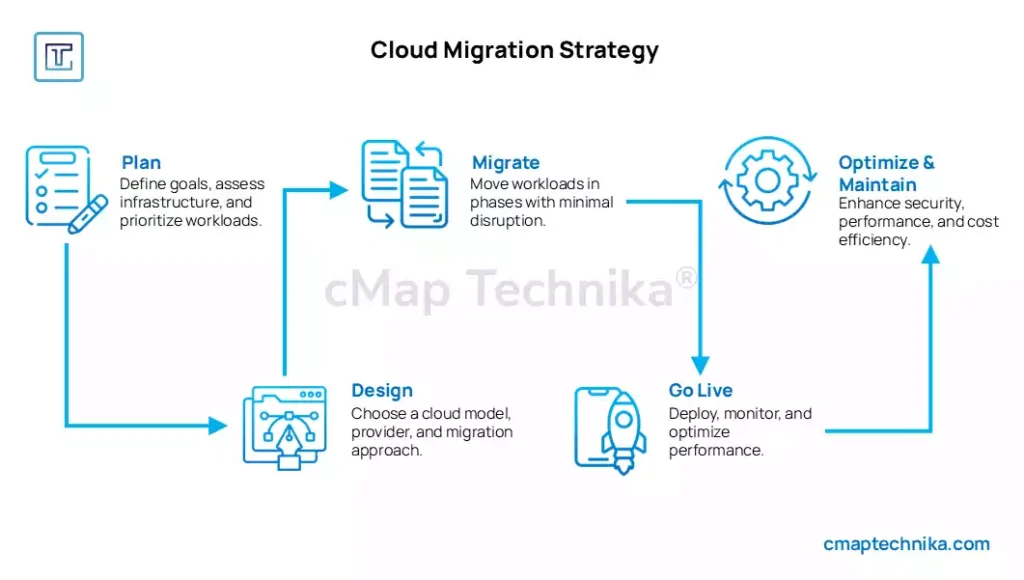
A well-structured migration strategy is critical for minimizing downtime, ensuring business continuity, and optimizing cloud benefits. Organizations should adopt a phased approach that aligns with their operational goals.
Migration Approaches:
- Rehosting (Lift-and-Shift): A quick and cost-effective way to migrate existing applications with minimal changes. While it provides a faster transition, it may not fully leverage cloud-native benefits.
- Replatforming: Involves minor optimizations, such as moving databases to managed cloud services, to improve performance without overhauling applications.
- Refactoring (Re-architecting): A more complex approach that redesigns applications to be cloud-native, leveraging microservices and serverless computing. While resource-intensive, this provides long-term efficiency and scalability.
Key Steps:
- Prioritize Workloads – Categorize applications based on business criticality and migration complexity. Start with low-risk, high-impact applications to gain quick wins.
- Develop a Phased Migration Plan – Avoid migrating everything at once. Instead, adopt an incremental approach that minimizes service disruptions.
- Establish a Rollback Strategy – Plan for contingencies by setting up fallback mechanisms in case of migration failures.
A clear strategy ensures a smooth transition, minimizing risks while maximizing cloud benefits.
4. Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
Data security is one of the biggest concerns during cloud migration. A robust security framework ensures data integrity, protects against cyber threats, and maintains regulatory compliance.
Best Practices:
- Implement Strong Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to safeguard sensitive information.
- Adopt Identity and Access Management (IAM): Restrict access based on user roles and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
- Ensure Compliance Adherence: Different industries have different regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR for data privacy, HIPAA for healthcare security, and ISO 27001 for information security management). Organizations must ensure their cloud setup aligns with these standards.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Proactively identify vulnerabilities and reinforce security controls through penetration testing and compliance checks.
By embedding security at every stage of migration, businesses can mitigate risks and build a resilient cloud infrastructure.
5. Optimizing Performance and Cost Efficiency
Once migration is complete, optimizing cloud resources is essential to maximize performance and control costs.
Key Strategies:
- Right-Sizing Resources: Avoid over-provisioning by selecting appropriate compute, storage, and networking resources. Continuous monitoring can help adjust capacity based on demand.
- Implement Auto-Scaling: Automatically scale resources up or down in response to workload fluctuations, ensuring optimal performance while minimizing waste.
- Utilize Cost Monitoring Tools: Leverage native cloud cost management solutions (e.g., AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management) to track spending and identify inefficiencies.
- Adopt Cloud-Native Features: Serverless computing, containerization, and microservices architectures can improve efficiency and reduce infrastructure overhead.
Optimizing cloud environments post-migration ensures long-term sustainability, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
6. Training Teams and Driving Adoption
A successful cloud transition is not just about technology—it also requires empowering teams with the right skills and fostering a cloud-first culture.
Key Actions:
- Provide Hands-On Training: Conduct workshops, certification programs, and real-world simulations to upskill IT and business teams on cloud platforms and best practices.
- Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage alignment between DevOps, security, and compliance teams to ensure seamless cloud adoption.
- Establish a Cloud Center of Excellence (CCoE): A dedicated team responsible for defining governance policies, best practices, and training initiatives to streamline cloud operations.
Investing in team enablement ensures smooth adoption and maximizes the return on cloud investments.
7. Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Cloud migration is not a one-time project—it requires ongoing monitoring and optimization to ensure continuous efficiency, security, and cost control.
Key Practices:
- Leverage Cloud Monitoring Tools: Utilize solutions like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, and Google Operations Suite to track performance metrics and identify anomalies.
- Automate Incident Detection and Response: AI-driven automation can proactively detect issues, trigger alerts, and resolve incidents with minimal human intervention.
- Conduct Periodic Cost and Security Reviews: Regular audits ensure that cloud expenses remain within budget and security measures evolve with emerging threats.
- Adapt to Business Needs: As organizational goals change, continuously refine cloud strategies to accommodate new workloads, technologies, and market dynamics.
By embracing a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can future-proof their cloud environments and sustain long-term success.
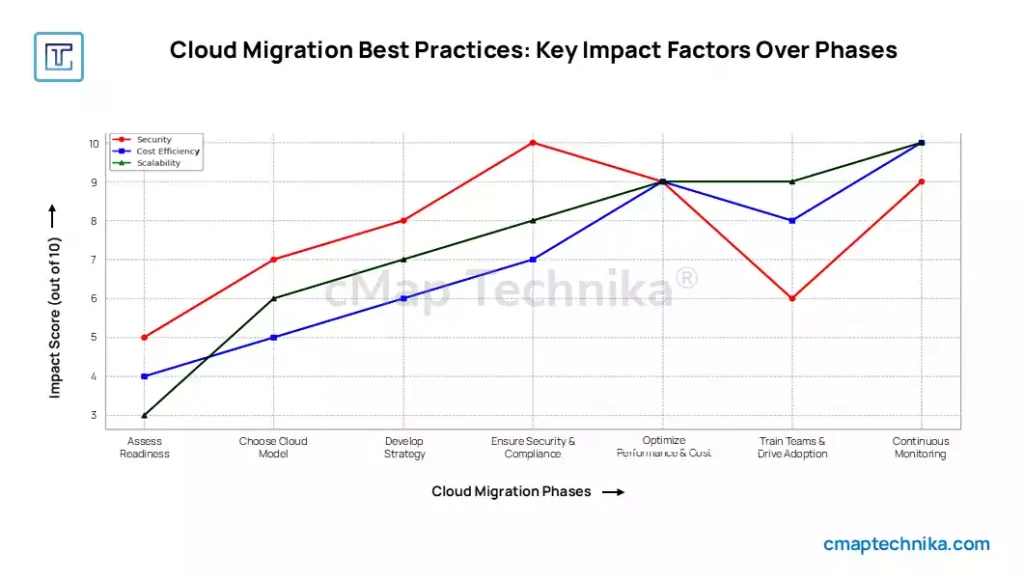
Conclusion
Cloud migration is more than just a technological shift—it is a strategic transformation that enables businesses to stay competitive in an increasingly digital world. A well-planned migration enhances agility, scalability, and cost efficiency while driving innovation and operational resilience.
By thoroughly assessing readiness, selecting the right cloud model, implementing robust security measures, and optimizing performance, organizations can ensure a smooth transition with minimal disruptions. However, cloud adoption does not end with migration; continuous monitoring, cost optimization, and workforce upskilling are critical to maximizing long-term value.
As technology evolves, businesses that embrace a proactive, adaptable cloud strategy will be better positioned to harness emerging innovations, mitigate risks, and sustain a future-ready digital ecosystem. Cloud migration is not just about moving workloads—it is about transforming the way organizations operate, innovate, and grow in the digital age.






