Introduction
In the competitive landscape of product development, the ability to scale effectively is a critical driver of long-term success. A product roadmap is more than just a plan—it’s a strategic tool that aligns business objectives with development efforts, ensuring that resources are used effectively and teams are working toward a shared vision.
However, building a roadmap that can scale with business growth and market shifts requires a structured approach, strong stakeholder alignment, and a deep understanding of customer needs. Scalable roadmaps must accommodate changes in user behavior, technological advancements, and competitive pressures while maintaining operational efficiency.
Leading tech companies like Amazon, Netflix, and Salesforce have demonstrated how a well-crafted product roadmap can drive sustained growth, market adaptability, and competitive advantage. This article explores key strategies for developing scalable product roadmaps, backed by real-world examples and case studies.
The Role of a Scalable Product Roadmap
A product roadmap serves as a strategic framework that outlines product development priorities, key milestones, and business goals over time. Unlike static roadmaps, scalable roadmaps are dynamic—they evolve based on market feedback, technological advancements, and internal business changes.
Core Benefits of a Scalable Product Roadmap:
- Strategic Alignment: Ensures that product development efforts align with business goals and market demands.
- Operational Efficiency: Optimizes resource allocation and reduces development bottlenecks.
- Market Adaptability: Enables quick responses to customer feedback and competitive pressures.
- Cross-Functional Clarity: Keeps product, marketing, sales, and engineering teams aligned on priorities.
Companies that fail to implement scalable roadmaps often struggle with delayed product launches, feature bloat, and missed market opportunities. A well-designed roadmap allows businesses to anticipate and respond to shifts in the market while maintaining development efficiency.
Key Elements of a Scalable Product Roadmap

1. Vision and Strategic Goals
A scalable roadmap starts with a clear product vision and long-term strategic goals. Defining the product’s market position, target audience, and core value proposition sets the foundation for effective decision-making.
Strategic goals must be ambitious yet achievable, providing a guiding framework for development efforts. These goals should be directly linked to business outcomes, such as revenue growth, market penetration, customer acquisition, and retention.
Example: Salesforce’s Customer 360 Strategy
Salesforce’s product roadmap revolves around its “Customer 360” vision—a unified customer relationship management (CRM) platform. This strategy focuses on integrating customer data across all Salesforce products to provide businesses with a comprehensive view of customer interactions. By defining a clear long-term goal, Salesforce aligned its development efforts with customer needs, leading to increased customer retention and higher average contract value (ACV).
The success of Salesforce’s Customer 360 strategy demonstrates how a clear vision creates alignment across product teams and drives consistent business outcomes. The company’s expansion into industries such as healthcare and financial services was made possible by a roadmap built around customer-centric data integration.
2. Customer-Centric Prioritization
Customer needs and market demands should drive the prioritization of features and updates. A scalable roadmap reflects both immediate customer feedback and long-term market trends.
Prioritization frameworks such as RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort) or MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) help product teams rank feature development based on business impact and customer value. Focusing on high-impact features ensures that development resources are used efficiently.
Example: Amazon’s Customer-First Roadmap
Amazon’s product roadmap consistently prioritizes customer convenience and service scalability. The company introduced features like one-click purchasing, same-day delivery, and Alexa voice ordering based on customer behavior analysis and market demand.
Amazon’s customer-centric approach to roadmap development allowed it to become the leading e-commerce platform globally. The decision to prioritize logistics infrastructure improvements—such as expanding fulfillment centers and refining delivery algorithms—was based on customer feedback about shipping speed and order accuracy. This alignment between product strategy and customer needs drove sustained market dominance.
3. Phased Rollouts and Incremental Development
Instead of launching a fully developed product at once, scalable roadmaps use phased rollouts to gather data, test performance, and refine features. Incremental development reduces risk and allows for course correction based on user feedback.
Phased rollouts allow businesses to validate product assumptions and minimize the risk of failure. A/B testing and user segmentation strategies can help refine feature performance before scaling to the broader user base.
Case Study: Netflix’s Content Recommendation Engine
Netflix’s recommendation algorithm was introduced through a phased rollout. The company initially tested the feature with a small subset of users, analyzing engagement and satisfaction before scaling to the broader user base.
Through continuous iteration, Netflix refined the algorithm using data on viewing habits, search patterns, and content preferences. This customer-driven development process enhanced user retention and increased average watch time. Today, Netflix’s recommendation engine is responsible for driving over 80% of viewed content, highlighting the importance of phased rollouts in building scalable product strategies.
4. Flexibility and Market Responsiveness
A scalable roadmap allows room for adjustments without losing strategic focus. Flexible frameworks like Agile and Lean development enable teams to adapt quickly to market changes and competitive shifts.
Market responsiveness requires real-time data analysis, competitive benchmarking, and rapid development cycles. Companies that build flexibility into their roadmaps can pivot more effectively in response to technological changes, regulatory shifts, or evolving customer needs.
Example: Tesla’s Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Tesla’s product roadmap includes the ability to modify vehicle software and performance through OTA updates. This flexible approach allows Tesla to improve battery performance, enhance autopilot functionality, and address security issues without requiring a physical recall.
Tesla’s roadmap flexibility has contributed to its market dominance in the electric vehicle (EV) sector. The ability to introduce new features and performance upgrades post-purchase has strengthened customer loyalty and extended the lifecycle value of Tesla vehicles.
Challenges in Building a Scalable Product Roadmap
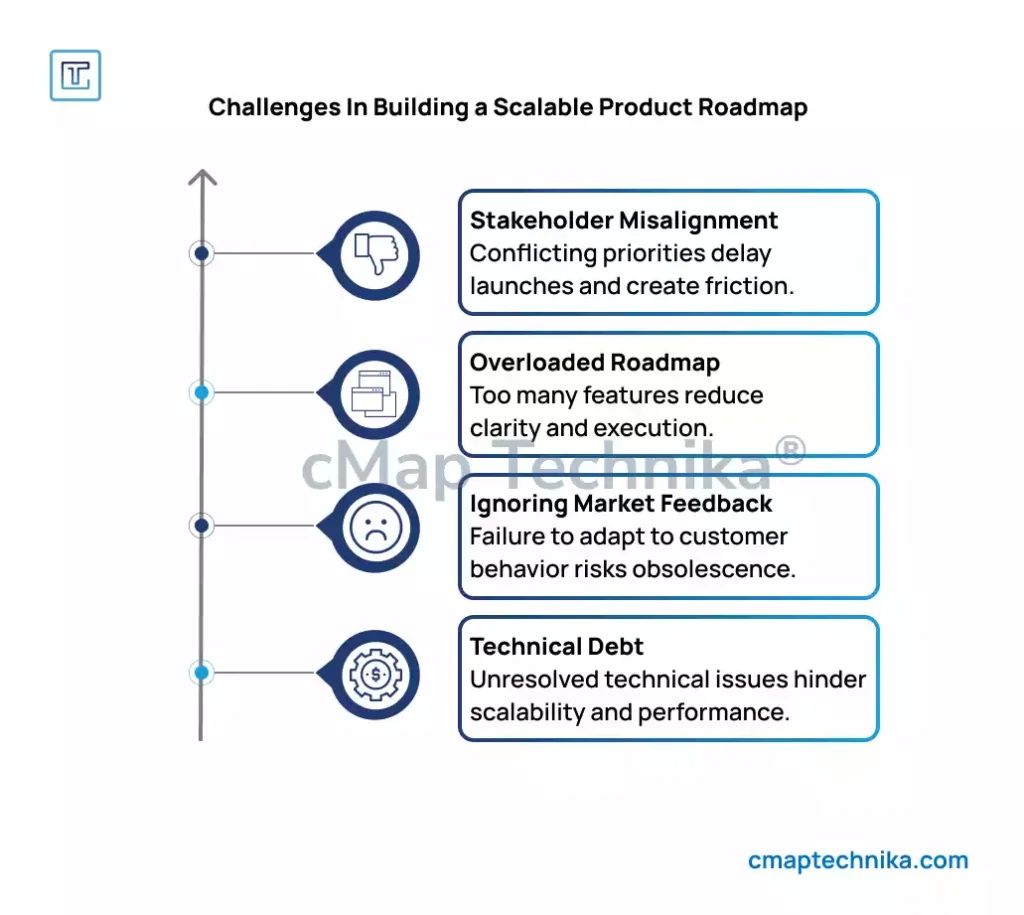
While a scalable roadmap offers strategic benefits, it also presents operational challenges:
- Stakeholder Misalignment: Conflicting priorities across product, marketing, and engineering teams can delay product launches and create friction.
- Overloading the Roadmap: Including too many features or conflicting goals can reduce clarity and execution efficiency.
- Neglecting Market Feedback: A roadmap that ignores customer behavior and market changes risks becoming outdated.
- Technical Debt: Adding new features without addressing underlying technical debt can reduce scalability and product performance.
Best Practices for Building a Scalable Product Roadmap
- Define Clear Strategic Goals
Establishing clear, measurable long-term objectives is essential for creating a scalable product roadmap. Start by identifying the business outcomes you want to achieve—whether it’s increasing market share, improving customer retention, or expanding into new markets. Strategic goals should be specific and aligned with broader business priorities. For example, Tesla’s strategic goal to lead the electric vehicle market drives its focus on battery innovation and autonomous driving features. By defining these high-level objectives, businesses can create a focused roadmap that guides product development and resource allocation. - Prioritize Based on Customer Impact
A successful product roadmap places customer value at the center of decision-making. Focus on features and updates that directly improve the user experience and provide measurable business value. Customer feedback, user behavior patterns, and support inquiries can help identify which updates will have the most impact. Amazon’s recommendation engine is a prime example—by analyzing customer purchase behavior, Amazon prioritized building a predictive system that now accounts for 35% of its sales. By aligning development priorities with customer needs, businesses can enhance user satisfaction and drive long-term loyalty. - Use Data to Guide Decisions
Data-driven decision-making is critical for building a scalable and adaptable roadmap. Leverage customer feedback, product usage patterns, and market trends to identify gaps and opportunities. A/B testing, cohort analysis, and performance metrics should inform which features to prioritize and how to adjust the product roadmap. Netflix’s content strategy is shaped by user data—patterns in viewing behavior and engagement levels drive decisions on content investment, leading to successful launches of shows like Stranger Things and The Witcher. This iterative, data-informed approach ensures that the product evolves to meet market demands. - Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
Product development is rarely confined to one department. Effective roadmaps require alignment between product, engineering, marketing, sales, and customer support teams. Cross-functional collaboration ensures that everyone is working toward the same strategic goals and prevents misalignment. For instance, Salesforce’s product updates are rolled out in close coordination with sales and customer success teams to ensure seamless customer onboarding and support. Regular communication and joint planning sessions help break down silos, improving execution and market responsiveness. - Maintain Flexibility
Market conditions, customer expectations, and competitive landscapes are constantly evolving—your roadmap should reflect that. Build flexibility into the roadmap by using phased rollouts and pilot programs to test and refine features before scaling. Spotify’s incremental release strategy for new features allows the company to test user response and make adjustments without overcommitting resources. This adaptive approach helps businesses respond quickly to market changes while minimizing risk. A flexible roadmap ensures that businesses can pivot when necessary without losing strategic focus.
By adopting these best practices, businesses can create a roadmap that is both strategic and adaptable, ensuring sustained growth and a competitive edge in a dynamic market.
Case Study: Spotify’s Agile Roadmap Strategy
Spotify’s product roadmap is structured around flexibility and user feedback. The company divides development into small, autonomous teams (known as “squads”) that focus on specific product areas, such as search, playlist curation, and social sharing.
This decentralized approach allows Spotify to test new features rapidly, respond to market trends, and make quick adjustments based on user engagement data. For example, Spotify’s rollout of the “Daily Mix” playlist feature began with small user segments before scaling to the broader user base.
Feedback from initial users helped the company fine-tune the playlist curation algorithm, increasing both user satisfaction and listening time. Spotify’s agile roadmap strategy has enabled the company to maintain a competitive edge in the highly saturated music streaming market.
Conclusion
A scalable product roadmap is not just a tool for guiding development—it’s a strategic asset that underpins long-term business success. Leading companies like Salesforce, Amazon, Netflix, Tesla, and Spotify have demonstrated that a well-structured roadmap enables businesses to adapt to changing market conditions, anticipate customer needs, and maintain a competitive edge. Salesforce’s customer-centric approach to product updates ensures that new features align with evolving user expectations, while Amazon’s phased product rollouts allow for rapid testing and refinement, ensuring market fit. Similarly, Netflix’s ability to leverage data-driven insights to adjust content strategies and Tesla’s over-the-air updates that improve vehicle performance in real time reflect the power of flexible and adaptive roadmaps.
A successful roadmap requires a balance of strategic foresight and operational flexibility. This involves setting clear long-term goals while allowing room for adjustments based on market feedback and technological advancements. It also means adopting a phased rollout strategy to test, iterate, and scale effectively while minimizing risk. Customer input must be at the core of the roadmap, with regular feedback loops to ensure that product evolution aligns with user expectations and delivers tangible value.
Moreover, businesses must incorporate cross-functional collaboration into the roadmap process, ensuring that product development, marketing, sales, and customer support are aligned on priorities and timelines. A scalable roadmap is not static—it should evolve based on performance metrics, market trends, and competitive analysis. This adaptability ensures that businesses remain innovative and responsive, even in the face of market disruptions.
By combining strategic vision with operational flexibility, businesses can create roadmaps that drive innovation, enhance customer satisfaction, and build sustainable competitive advantage. The success of industry leaders underscores the importance of a dynamic, scalable approach to product development—one that not only meets current market demands but also positions the business to capitalize on future opportunities.







