Introduction
Cloud computing has become the backbone of modern digital transformation, enabling organizations to enhance agility, optimize costs, and scale operations efficiently. As cloud adoption accelerates across industries, businesses must carefully evaluate their cloud provider options to align with operational needs and long-term goals.
Among the leading cloud platforms, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure have emerged as dominant forces in the market. AWS, as the pioneer of cloud computing, has established itself as the most widely adopted cloud provider globally, offering an extensive range of services and a vast infrastructure network. On the other hand, Microsoft Azure has gained significant traction, particularly within enterprises already integrated into the Microsoft ecosystem, providing seamless compatibility with Windows-based applications, Office 365, and enterprise security frameworks.
Choosing between Azure and AWS requires a thorough understanding of key factors such as market share, service offerings, pricing structures, security frameworks, and scalability options. Each platform has distinct advantages in areas such as computing power, AI capabilities, hybrid cloud support, and compliance regulations. While AWS provides a mature, globally distributed infrastructure with a strong developer ecosystem, Azure offers deep enterprise integrations and hybrid cloud flexibility.
This report delivers an in-depth comparative analysis of Azure and AWS, evaluating their strengths, challenges, and ideal use cases. By examining their performance, cost efficiency, governance capabilities, and future market trends, businesses can make informed decisions about which cloud provider best aligns with their digital transformation strategy.
2. Market Share and Industry Adoption
2.1 Global Market Overview
AWS, launched in 2006, was the first major cloud service provider and continues to lead the market in terms of adoption and revenue. Azure, introduced by Microsoft in 2010, has steadily gained traction, particularly among enterprises with existing Microsoft ecosystems.
2.2 Adoption Trends
- AWS: Preferred by startups, technology firms, and businesses requiring high scalability and diverse service offerings.
- Azure: Popular among enterprises, especially those already using Microsoft products like Windows Server, Active Directory, and Office 365.
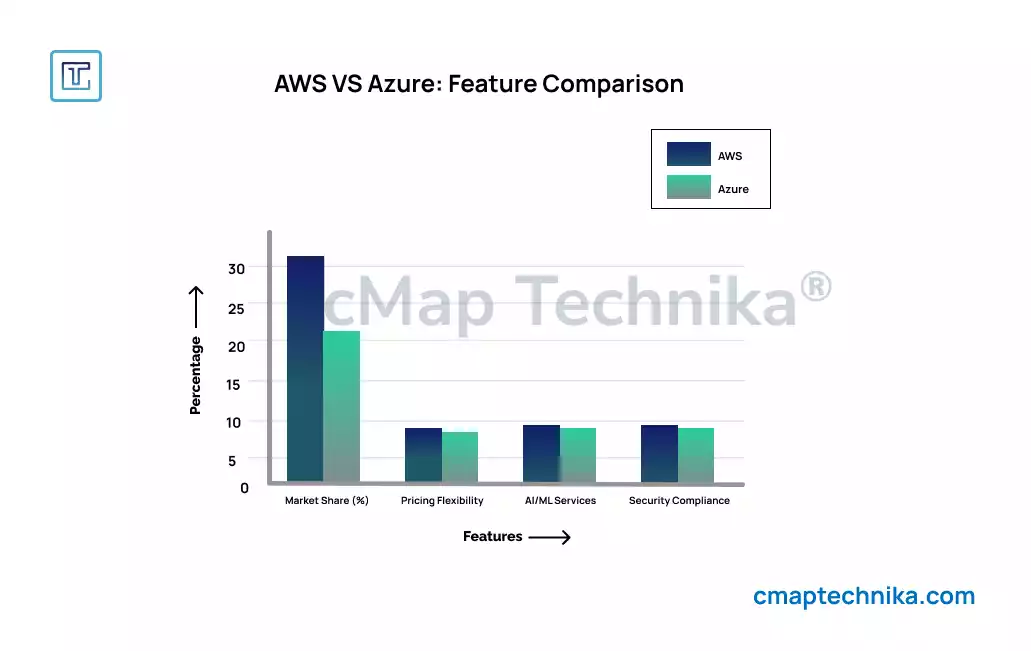
3. Service Offerings and Capabilities
3.1 Compute Services
- AWS: Amazon EC2 provides a wide range of instance types, offering flexibility in workload optimization. AWS Lambda enables serverless computing for event-driven applications.
- Azure: Azure Virtual Machines support both Windows and Linux environments, and Azure Functions offer serverless capabilities similar to AWS Lambda.
3.2 Storage Solutions
- AWS: Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is a highly scalable object storage solution, while Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store) supports persistent block storage.
- Azure: Azure Blob Storage competes with Amazon S3, and Azure Disk Storage provides block storage capabilities comparable to AWS EBS.
3.3 Networking and Content Delivery
- AWS: Offers Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) for networking and Amazon CloudFront for content delivery.
- Azure: Provides Azure Virtual Network and Azure CDN (Content Delivery Network) for similar functionalities.
3.4 AI and Machine Learning
- AWS: Amazon SageMaker simplifies building and training machine learning models.
- Azure: Azure Machine Learning offers a managed cloud-based environment for ML model development.
4. Pricing Comparison
Cloud pricing is complex due to various factors such as usage patterns, storage, compute power, and network traffic. Both Azure and AWS provide pay-as-you-go models, reserved instances for long-term savings, and free-tier options.
4.1 AWS Pricing
- Charges per-second billing for EC2 instances.
- Offers cost-saving programs like AWS Savings Plans and Spot Instances.
4.2 Azure Pricing
- Charges per-minute billing for Virtual Machines.
- Provides Hybrid Benefit discounts for customers with existing Microsoft licenses.
Cost Considerations: Azure may be more cost-effective for organizations already using Microsoft software, whereas AWS offers better flexibility in instance types and pricing models.
5. Security and Compliance
Both Azure and AWS prioritize security and compliance, offering robust encryption, identity management, and regulatory compliance certifications.
5.1 AWS Security
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) enables fine-grained access control.
- AWS Shield provides DDoS protection.
- Compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and SOC standards.
5.2 Azure Security
- Azure Active Directory offers identity management.
- Azure Security Center provides threat protection.
- Compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, FedRAMP, and more.
Security Verdict: Azure integrates seamlessly with Microsoft’s enterprise security tools, while AWS offers more advanced security automation options.
6. Performance and Reliability
Both providers operate vast global infrastructures with data centers worldwide to ensure high availability and disaster recovery.
- AWS: Leads in availability zones and global infrastructure, ensuring high uptime.
- Azure: Has a strong presence in enterprise data centers, offering hybrid cloud advantages.
7. Use Cases and Industry Applications
Both AWS and Azure offer robust cloud services, but their strengths cater to different business needs and industry requirements. Organizations must assess their existing infrastructure, operational priorities, and future growth strategies to determine the most suitable platform.
7.1 When to Choose AWS
AWS is the preferred choice for organizations that prioritize scalability, innovation, and a vast ecosystem of cloud-native services. It is particularly advantageous for startups, technology-driven companies, and enterprises with extensive cloud-based workloads.
- Startups and High-Growth Companies
AWS provides an ideal environment for startups and tech companies that need highly scalable infrastructure without upfront capital investment. With services like Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling and AWS Lambda, businesses can dynamically adjust computing resources based on demand. Additionally, AWS Activate offers startup-focused credits, technical support, and mentorship. - Cloud-Native and Digital-First Enterprises
Organizations that operate primarily in the cloud, such as SaaS companies, media streaming platforms, and e-commerce businesses, benefit from AWS’s mature infrastructure and vast service catalog. Features like AWS Global Accelerator and CloudFront CDN enhance performance, ensuring seamless content delivery across global audiences. - AI/ML and Big Data Analytics
AWS offers Amazon SageMaker, a powerful platform for machine learning model development and deployment. Its AWS Glue service simplifies ETL processes, enabling businesses to build scalable data lakes and real-time analytics pipelines. Enterprises leveraging AI/ML for predictive analytics, automation, and personalization find AWS’s ecosystem highly efficient. - Businesses Requiring Global Reach
With the largest global infrastructure footprint, AWS is well-suited for multinational corporations that need low-latency access to cloud resources. Its extensive network of Availability Zones and Edge Locations ensures reliability and redundancy, making it an excellent choice for businesses with a distributed user base.
7.2 When to Choose Azure
Azure is the preferred cloud platform for organizations deeply embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem, as well as industries requiring hybrid cloud solutions, regulatory compliance, and enterprise-grade security.
- Enterprises with Existing Microsoft Investments
Businesses that rely on Windows Server, Active Directory, SQL Server, Microsoft 365, and Dynamics 365 benefit from Azure’s seamless integration. Azure Hybrid Benefit allows organizations to use their existing on-premise Windows and SQL Server licenses in the cloud, reducing costs while maintaining consistency. - Hybrid Cloud and On-Premise Integration
Organizations that require a hybrid approach—balancing on-premise and cloud workloads—find Azure’s Azure Arc and Azure Stack particularly advantageous. These services enable businesses to extend Azure capabilities to on-premise data centers, facilitating edge computing, legacy system modernization, and regulatory compliance. - Industries with Stringent Compliance and Security Needs
Azure is well-suited for government agencies, healthcare organizations, and financial institutions that must adhere to strict regulatory frameworks. It offers specialized compliance certifications, including FedRAMP, HIPAA, GDPR, and ISO 27001, ensuring data governance and security standards are met. - Businesses Leveraging Advanced AI and Business Intelligence
While AWS has SageMaker, Azure provides Azure AI and Power BI, which are tightly integrated with enterprise applications. Organizations that prioritize AI-driven business insights, automation, and natural language processing can leverage Azure Cognitive Services to enhance customer engagement and operational efficiency. - Large-Scale Enterprise IT Modernization
Companies undergoing large-scale digital transformation projects benefit from Azure’s ability to integrate seamlessly with legacy enterprise systems while offering a pathway to cloud-native architectures. Tools like Azure DevOps and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) support modern development methodologies, including CI/CD pipelines and containerization.
Final Considerations
While AWS and Azure serve diverse use cases, businesses should evaluate factors such as pricing, existing IT infrastructure, data sovereignty, compliance requirements, and long-term scalability before making a decision. Some organizations adopt a multi-cloud strategy, leveraging the strengths of both platforms for different workloads, ensuring business continuity, vendor diversification, and risk mitigation.
8. Conclusion: Which One Powers Your Future?
Both AWS and Azure offer powerful cloud solutions, each excelling in different areas. AWS maintains a strong lead in scalability, service variety, and developer-friendly tools, making it ideal for tech-driven startups and global enterprises. Azure, on the other hand, is the preferred choice for businesses with existing Microsoft investments, offering seamless integration with Microsoft’s enterprise ecosystem.
Ultimately, the choice between AWS and Azure depends on an organization’s specific needs, cost considerations, and existing IT infrastructure. Businesses should assess their workload requirements, security priorities, and long-term scalability goals before selecting the right cloud partner.Final Recommendation: For maximum flexibility and broad service offerings, AWS is the leader. However, for enterprises leveraging Microsoft technology, Azure provides unmatched compatibility and efficiency. The future of cloud computing is dynamic, and businesses must continuously evaluate their cloud strategies to stay ahead in the evolving digital landscape.






