Introduction
In the fast-paced world of software development, speed and efficiency are critical to maintaining a competitive edge. Traditional development and operations (DevOps) processes often struggle to keep up with growing complexity, leading to bottlenecks, inconsistent releases, and increased error rates. DevOps automation addresses these challenges by streamlining workflows, automating repetitive tasks, and improving collaboration between development and operations teams. This article explores how DevOps automation works, the key components involved, and how it transforms development and operations, using real-world examples to illustrate its impact.
What Is DevOps Automation?
DevOps automation refers to the use of tools and technologies to automate the processes involved in software development, testing, deployment, and infrastructure management. The goal is to eliminate manual errors, accelerate release cycles, and create a more consistent development environment.
Key Elements of DevOps Automation:

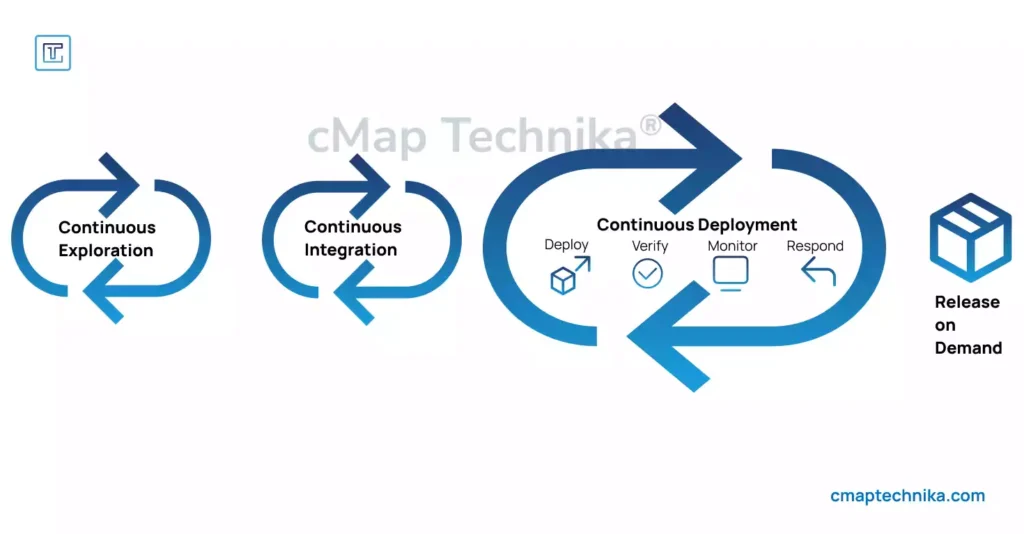
- Continuous Integration (CI): Automating the integration of code changes into a shared repository to detect and fix bugs early.
- Continuous Deployment (CD): Automatically deploying code to production once it passes testing, reducing the time between development and release.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Managing infrastructure through code to ensure consistency and scalability.
- Automated Testing: Running unit tests, functional tests, and performance tests automatically to identify issues before deployment.
- Monitoring and Feedback: Using automated tools to track system performance and gather real-time feedback for continuous improvement.
How DevOps Automation Improves Development and Operations
Automation fundamentally transforms how development and operations teams work, increasing efficiency, consistency, and scalability.
1. Accelerated Deployment Cycles
Before automation, development teams relied on manual deployment processes, which were time-consuming and prone to human error. DevOps automation reduces deployment times from days or weeks to minutes or hours.
Example:
Netflix implemented an automated CI/CD pipeline to handle over 500 code releases per day. Their automation tools automatically test, build, and deploy code across their global infrastructure, allowing engineers to focus on improving user experience rather than handling manual updates.
2. Improved Code Quality and Stability
Automated testing and integration catch issues early in the development cycle, reducing the risk of bugs and system failures post-release. This improves both the quality and reliability of code.
Example:
Google’s DevOps team uses automated testing suites to run thousands of tests in parallel. This ensures that even minor code changes are vetted for performance and security issues before reaching production, reducing post-release failures by over 60%.
3. Enhanced Collaboration Between Teams
Automation tools enable better communication and visibility between development and operations teams by centralizing data and streamlining feedback loops.
Example:
Spotify adopted a “Squad Model” where cross-functional teams handle development, testing, and operations. They use Jenkins for CI/CD and Grafana for monitoring, creating a unified feedback loop that allows faster problem resolution and higher product stability.
4. Cost and Resource Optimization
By automating infrastructure provisioning and management, organizations can reduce operational costs and minimize wasted resources.
Example:
Capital One implemented Infrastructure as Code (IaC) using Terraform. This allowed them to automate server provisioning and scaling, reducing cloud infrastructure costs by over 30% while maintaining uptime during traffic spikes.
5. Faster Recovery and Rollback
Automated monitoring and rollback mechanisms allow for quick identification and resolution of issues, minimizing downtime.
Example:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) uses automated rollback protocols that can revert faulty updates within seconds. This ensures high availability and reduces customer impact from service disruptions.
Challenges of Implementing DevOps Automation
While DevOps automation offers significant advantages, implementing it effectively requires addressing several challenges:
1. Complexity of Tool Integration
- DevOps automation involves integrating multiple tools for CI/CD, testing, and monitoring.
- Solution: Choose a standardized toolset like Jenkins, Ansible, and Kubernetes to minimize compatibility issues.
2. Skill Gaps in Automation
- Automating DevOps processes requires specialized skills in coding, infrastructure management, and tool configuration.
- Solution: Invest in employee training and hire experienced DevOps engineers.
3. Security and Compliance Risks
- Automated deployments can introduce security vulnerabilities if misconfigured.
- Solution: Implement automated security checks and penetration testing as part of the CI/CD pipeline.
Best Practices for Effective DevOps Automation
To maximize the benefits of DevOps automation, organizations should adopt the following best practices:
Start with a Small, Controlled Rollout
- Begin automation with a single pipeline or small-scale project to identify and resolve issues early.
Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for Consistency
- Automate infrastructure provisioning to avoid configuration drift and ensure consistent environments.
Establish Clear Metrics and KPIs
- Measure deployment frequency, mean time to recovery (MTTR), and failure rates to track progress and refine automation strategies.
Automate Security and Compliance
- Integrate automated security scans and compliance checks into the CI/CD pipeline to identify vulnerabilities early.
Encourage a Culture of Collaboration
- Create a shared responsibility model where development and operations teams work together to manage automation and improve system performance.
Real-World Case Study: Netflix’s DevOps Automation Success
Netflix is a prime example of a company leveraging DevOps automation to maintain a competitive edge. They handle over 500 billion content requests daily and rely heavily on automated CI/CD pipelines to ensure service stability and quick deployment of new features.
How Netflix Uses DevOps Automation:
- Spinnaker – Netflix’s open-source CD platform automates the entire release process.
- Chaos Monkey – An automated testing tool that randomly shuts down services to test system resilience.
- Atlas – A real-time monitoring platform that tracks application performance and identifies issues before they affect users.
Results:
- Increased deployment frequency from once a week to over 500 deployments per day.
- Reduced mean time to recovery (MTTR) from several hours to a few minutes.
- Improved customer satisfaction due to faster bug fixes and feature updates.
Conclusion
DevOps automation is transforming the way organizations develop, test, and deploy software. By automating repetitive tasks, enhancing collaboration, and improving code quality, DevOps automation helps companies achieve faster releases, higher stability, and lower operational costs. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, the right tools, and a strong DevOps culture. Companies like Netflix, Google, and Capital One demonstrate that with the right approach, DevOps automation can drive significant business value and competitive advantage.






