How to Apply Agile Frameworks for Product Success
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced and competitive market, the ability to adapt quickly to changing customer demands and technological advancements has become a key determinant of product success. Traditional product management models, which rely on rigid planning and long development cycles, often fail to keep pace with these dynamic market conditions. Agile product management offers a solution by providing a flexible, iterative framework that enables product teams to deliver value faster, incorporate real-time customer feedback, and adapt to market changes with greater efficiency.
The rise of companies like Spotify, Amazon, and Slack illustrates how adopting Agile frameworks can lead to significant competitive advantages. Agile isn’t just a methodology—it’s a mindset that encourages continuous improvement, customer-centric development, and rapid problem-solving. This article explores the core Agile frameworks—Scrum, Kanban, and SAFe—and provides practical insights on how product managers can apply them to build scalable, customer-focused products. By mastering Agile principles, product managers can drive innovation, improve customer satisfaction, and position their products for long-term success.
What is Agile in Product Management?
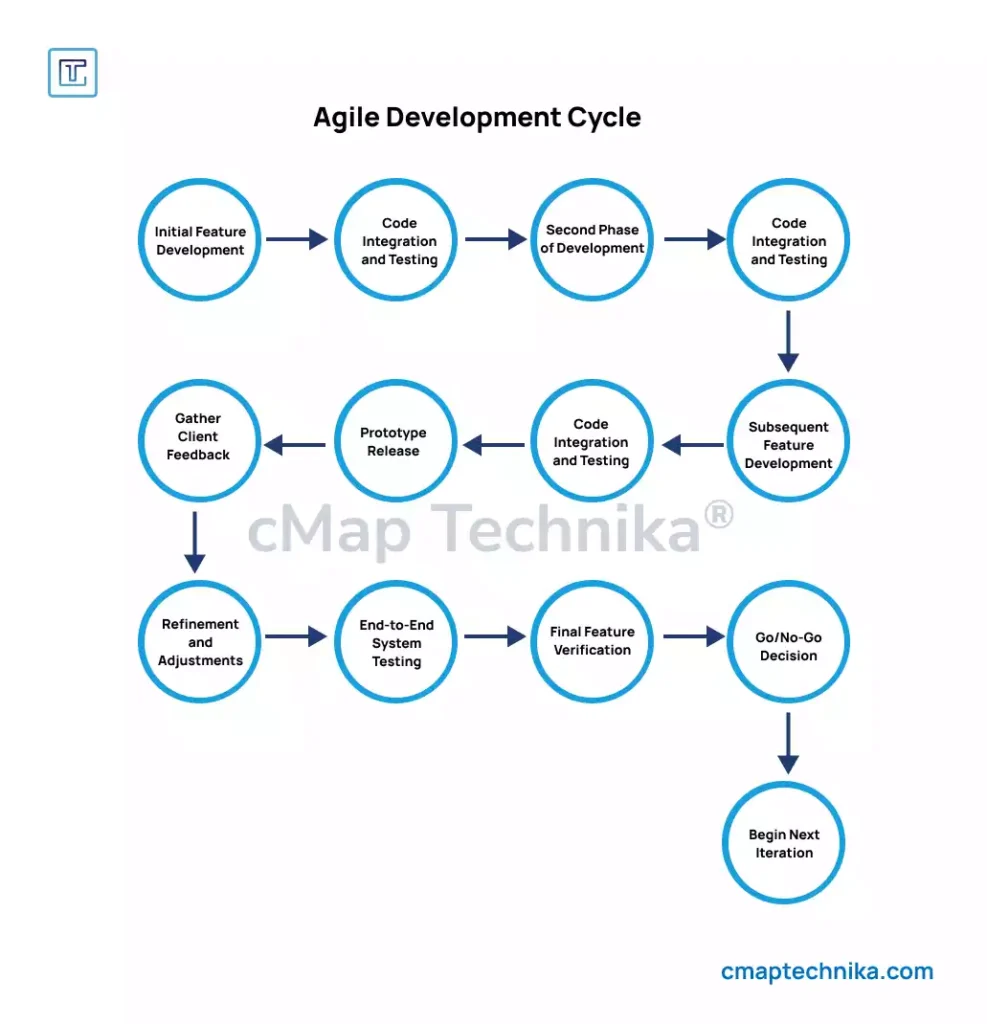
Agile product management is an iterative approach that enables product managers to adapt to changing customer needs, market dynamics, and business goals. Unlike traditional waterfall methods, which follow a linear development cycle, Agile focuses on continuous improvement, rapid feedback, and delivering value incrementally.
Agile principles center around:
Embracing Change: Treating changes in customer needs or market shifts as opportunities rather than obstacles.
Customer Collaboration: Direct and frequent communication with customers to gather feedback and adjust product features accordingly.
Iterative Development: Dividing product development into smaller cycles or sprints to allow flexibility and quick adjustments.
Cross-Functional Teams: Encouraging collaboration between product, engineering, design, and marketing to improve decision-making and execution speed.
Key Agile Frameworks
Agile product management involves applying specific frameworks that structure how teams operate, prioritize tasks, and deliver value. The most widely used frameworks include Scrum, Kanban, and SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework).

In the chart above, the ideal trend line shows the expected rate of progress, while the actual progress line reflects real-time task completion. Teams use this to stay on track and address issues early.
This kind of chart is commonly used in Scrum, one of the most widely adopted Agile methodologies.
1. Scrum
Scrum is the most popular Agile framework, particularly suited for software development and complex product environments. It emphasizes time-boxed sprints and defined roles within the team.
How It Works:
- A Product Owner defines product backlog items (features, improvements, bugs).
- The team conducts a Sprint Planning session to select backlog items for the sprint.
- Daily Scrum Meetings (stand-ups) allow the team to sync progress and address roadblocks.
- A Sprint Review at the end evaluates progress and gathers stakeholder feedback.
- A Sprint Retrospective focuses on process improvements for the next sprint.
Example:
Spotify has successfully used Scrum to manage its music streaming platform. Cross-functional squads focus on specific features, like playlist generation or user recommendations. By working in short sprints, they continuously improve the user experience and respond quickly to market changes.
2. Kanban
Kanban focuses on visualizing workflow and limiting work in progress (WIP) to improve efficiency and reduce bottlenecks. It’s highly flexible and ideal for teams handling continuous delivery.
How It Works:
- Teams use a Kanban Board to visualize tasks.
- Work is broken into stages (e.g., To-Do, In Progress, Completed).
- The team limits WIP to prevent overloading and ensures smooth workflow.
- Continuous monitoring helps teams identify and resolve bottlenecks quickly.
Example:
Toyota pioneered the Kanban system for manufacturing. Its Just-in-Time (JIT) production model reduced waste and improved inventory management by ensuring that production was closely aligned with demand.
3. SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework)

SAFe helps large organizations implement Agile across multiple teams and departments. It’s designed to align business strategy with execution through structured roles, cadences, and ceremonies.
How It Works:
- Product teams work within an Agile Release Train (ART) that delivers incremental value in fixed cycles (Program Increments).
- Cross-functional teams collaborate under a unified product vision.
- Regular synchronization ensures alignment between product development and business goals.
Example:
Intel adopted SAFe to streamline its semiconductor product development. By aligning engineering, product, and business teams under a unified framework, Intel reduced time-to-market and improved overall product quality.
Applying Agile in Product Management
1. Define Clear Objectives and Metrics
Successful Agile implementation starts with well-defined goals that guide product development and ensure alignment with business priorities. Without clear objectives, product teams may struggle to balance feature development with market needs.
Product managers should identify key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
- Customer Satisfaction: Measured through Net Promoter Score (NPS) and customer surveys.
- Feature Adoption Rate: Tracks how quickly and widely new features are adopted by users.
- Time-to-Market: Measures how quickly new updates and features reach customers.
For example, Amazon sets clear objectives for customer experience, such as reducing checkout time and improving product search accuracy. Agile teams are measured against these KPIs to ensure alignment with business goals and customer satisfaction. By defining measurable outcomes, Amazon ensures that product teams remain focused on delivering tangible value to users.
2. Establish a Prioritization Framework
Agile product managers must balance customer needs, business value, and technical feasibility. Without a clear prioritization framework, teams can become overwhelmed with competing demands and lose focus on core business goals.
Popular prioritization methods include:
- MoSCoW (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won’t have): Helps teams focus on essential features while deferring less critical tasks.
- Value vs. Effort: Prioritizes features based on their potential impact versus development effort.
- RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort): Assigns scores based on potential reach, business impact, confidence in success, and required effort.
For example, Netflix used a value vs. effort framework to prioritize the release of offline viewing. Market demand and competitive positioning made this feature a high-value target. After assessing development complexity, Netflix launched the feature quickly, increasing customer retention and competitive advantage.
3. Foster a Feedback Loop
Regular customer feedback ensures that products evolve based on actual user behavior and market demands. Agile frameworks emphasize early testing and quick iterations to integrate this feedback into product development.
Best practices for establishing a feedback loop include:
- Beta Testing: Allows select customers to test new features before full release.
- User Interviews and Surveys: Gathers direct input on product experience.
- Analytics and Heatmaps: Provides insights into user behavior and feature performance.
For example, Dropbox relies heavily on beta testing and real-time feedback to shape product updates. When launching its new file-sharing feature, Dropbox invited power users to test functionality and provide feedback. Rapid iterations based on user suggestions resulted in a more intuitive user interface and higher adoption rates.
4. Empower Cross-Functional Teams
Agile thrives on collaboration between product managers, engineers, designers, and marketers. Cross-functional teams enable faster decision-making and a holistic view of the product lifecycle.
For a product to succeed, all stakeholders must be aligned on goals, priorities, and execution timelines. Key strategies include:
- Daily Stand-Ups: Short meetings where each team member shares progress and roadblocks.
- Joint Roadmap Planning: Ensures that development, design, and marketing teams work toward a shared vision.
- Clear Accountability: Each team member knows their specific role and contribution to product success.
For example, Slack’s product teams include developers, designers, and customer support staff. This structure allows Slack to address both technical issues and customer experience improvements simultaneously. The result is a faster product release cycle and improved user engagement.
5. Adapt and Evolve
Markets and customer needs are constantly changing. An Agile product roadmap must be flexible enough to adapt to new challenges and opportunities. Product managers should:
- Regularly Review Roadmaps: Ensure alignment with shifting market conditions.
- Evaluate Performance: Monitor product performance and user feedback to adjust priorities.
- Embrace Failure: Treat setbacks as learning opportunities and adjust strategies accordingly.
For example, Tesla constantly adapts its product roadmap based on technological advancements and market feedback. By rapidly adjusting production strategies and feature releases, Tesla maintains a competitive edge in the electric vehicle market.
Conclusion
Mastering Agile in product management requires more than implementing a framework—it demands a shift in strategy, culture, and execution. Companies like Spotify, Amazon, Tesla, and Slack demonstrate that Agile frameworks, when properly applied, create a foundation for sustained growth and market responsiveness. Agile enables product teams to deliver value faster, adapt to market changes, and engage more effectively with customers.
Successful Agile product management hinges on defining clear objectives, empowering cross-functional teams, fostering continuous feedback, and maintaining flexibility. An effective Agile roadmap aligns product development with business goals while remaining adaptable to new opportunities and challenges. By embracing Agile principles, product managers can create products that not only meet customer needs but also drive competitive advantage and long-term business success.







